Unraveling the genetic complexity of Drosophila stardust during photoreceptor morphogenesis and prevention of light-induced degeneration
- PMID: 17603117
- PMCID: PMC1950624
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.107.071449
Unraveling the genetic complexity of Drosophila stardust during photoreceptor morphogenesis and prevention of light-induced degeneration
Abstract
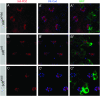
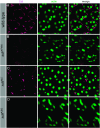
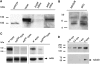
Drosophila Stardust, a membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK), recruits the transmembrane protein Crumbs and the cytoplasmic proteins DPATJ and DLin-7 into an apically localized protein scaffold. This evolutionarily conserved complex is required for epithelial cell polarity in Drosophila embryos and mammalian cells in culture. In addition, mutations in Drosophila crumbs and DPATJ impair morphogenesis of photoreceptor cells (PRCs) and result in light-dependent retinal degeneration. Here we show that stardust is a genetically complex locus. While all alleles tested perturb epithelial cell polarity in the embryo, only a subset of them affects morphogenesis of PRCs or induces light-dependent retinal degeneration. Alleles retaining particular postembryonic functions still express some Stardust protein in pupal and/or adult eyes. The phenotypic complexity is reflected by the expression of distinct splice variants at different developmental stages. All proteins expressed in the retina contain the PSD95, Discs Large, ZO-1 (PDZ), Src homology 3 (SH3), and guanylate kinase (GUK) domain, but lack a large region in the N terminus encoded by one exon. These results suggest that Stardust-based protein scaffolds are dynamic, which is not only mediated by multiple interaction partners, but in addition by various forms of the Stardust protein itself.
Figures



References
-
- Aartsen, W. M., A. Kantardzhieva, J. Klooster, A. G. van Rossum, S. A. van de Pavert et al., 2006. Mpp4 recruits Psd95 and Veli3 towards the photoreceptor synapse. Hum. Mol. Genet. 15: 1291–1302. - PubMed
-
- Alloway, P. G., L. Howard and P. J. Dolph, 2000. The formation of stable rhodopsin-arrestin complexes induces apoptosis and photoreceptor cell degeneration. Neuron 28: 129–138. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann, A., M. Schneider, F. Grawe, E. Theilenberg and E. Knust, 2001. Drosophila Stardust is a partner of Crumbs in the control of epithelial cell polarity. Nature 414: 638–643. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann, A., M. Timmer, J. Sierralta, G. Pietrini, E. D. Gundelfinger et al., 2004. Cell type-specific recruitment of Drosophila Lin-7 to distinct MAGUK-based protein complexes defines novel roles for Sdt and Dlg-S97. J. Cell Sci. 117: 1899–1909. - PubMed
-
- Bilder, D., M. Schober and N. Perrimon, 2003. Integrated activity of PDZ protein complexes regulates epithelial polarity. Nat. Cell Biol. 5: 53–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

