Concentration gradient along the scala tympani after local application of gentamicin to the round window membrane
- PMID: 17603318
- PMCID: PMC2728588
- DOI: 10.1097/MLG.0b013e318058a06b
Concentration gradient along the scala tympani after local application of gentamicin to the round window membrane
Abstract
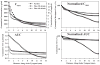
Objectives: The distribution of gentamicin along the fluid spaces of the cochlea after local applications has never previously been demonstrated. Computer simulations have predicted that significant basal-apical concentration gradients might be expected, and histologic studies indicate that hair cell damage is greater at the base than at the apex after local gentamicin application. In the present study, gradients of gentamicin along the cochlea were measured.
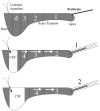
Methods: A recently developed method of sampling perilymph from the cochlear apex of guinea pigs was used in which the samples represent fluid originating from different regions along the scala tympani. Gentamicin concentration was determined in sequential apical samples that were taken after up to 3 hours of local application to the round window niche.
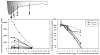
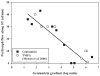
Results: Substantial gradients of gentamicin along the length of the scala tympani were demonstrated and quantified, averaging more than 4,000 times greater concentration at the base compared with the apex at the time of sampling. Peak concentrations and gradients for gentamicin varied considerably between animals, likely resulting from variations in round window membrane permeability and rates of perilymph flow.
Conclusions: The large gradients for gentamicin demonstrated here in guinea pigs account for how it is possible to suppress vestibular function in some patients with a local application of gentamicin without damaging auditory function. Variations in round window membrane permeability and in perilymph flow could account for why hearing losses are observed in some patients.
Figures
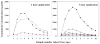



References
-
- Chia SH, Gamst AC, Anderson JP, Harris JP. Intratympanic Gentamicin Therapy for Meniere’s Disease: A Meta-analysis. Otol Neurotol. 2004;25:544–552. - PubMed
-
- Schoendorf J, Neugebauer P, Michel O. Continuous intratympanic infusion of gentamicin via a microcatheter in Menière’s disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001;124:203–207. - PubMed
-
- Hoffer ME, Balough B, Henderson J, et al. Use of sustained release vehicles in the treatment of Meniere’s disease. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1997;30:1159–66. - PubMed
-
- Plontke SKR, Wood AW, Salt AN. Analysis of gentamicin kinetics in fluids of the inner ear with round window administration. Otology and Neurotology. 2002;23:967–974. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

