Telomerase and its potential for therapeutic intervention
- PMID: 17603541
- PMCID: PMC2095101
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707374
Telomerase and its potential for therapeutic intervention
Abstract
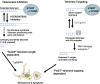
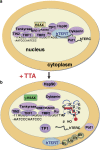
Telomerase and telomeres are attractive targets for anticancer therapy. This is supported by the fact that the majority of human cancers express the enzyme telomerase which is essential to maintain their telomere length and thus, to ensure indefinite cell proliferation--a hallmark of cancer. Tumours have relatively shorter telomeres compared to normal cell types, opening the possibility that human cancers may be considerably more susceptible to killing by agents that inhibit telomere replication than normal cells. Advances in the understanding of the regulation of telomerase activity and the telomere structure, as well as the identification of telomerase and telomere associated binding proteins have opened new avenues for therapeutic intervention. Here, we review telomere and telomerase biology and the various approaches which have been developed to inhibit the telomere/telomerase complex over the past decade. They include inhibitors of the enzyme catalytic subunit and RNA component, agents that target telomeres, telomerase vaccines and drugs targeting binding proteins. The emerging role of telomerase in cancer stem cells and the implications for cancer therapy are also discussed.
Figures
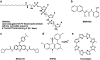
References
-
- Armanios M, Greider CW. Telomerase and cancer stem cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2005;70:205–208. - PubMed
-
- Bisoffi M, Heaphy CM, Griffith JK. Telomeres: prognostic markers for solid tumours. Int J Cancer. 2006;119:2255–2260. - PubMed
-
- Blackburn EH. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature. 1991;305:569–573. - PubMed
-
- Blackburn EH. Telomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:113–129. - PubMed
-
- Blackburn EH. Telomere states and cell fates. Nature. 2000;408:53–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

