Myosin light chain kinase-independent inhibition by ML-9 of murine TRPC6 channels expressed in HEK293 cells
- PMID: 17603544
- PMCID: PMC1978268
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707368
Myosin light chain kinase-independent inhibition by ML-9 of murine TRPC6 channels expressed in HEK293 cells
Abstract
Background and purpose: Myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) plays a pivotal role in regulation of cellular functions, the evidence often relying on the effects of extracelluarly administered drugs such as ML-9. Here we report that this compound exerts non-specific inhibitory actions on the TRPC6 channel, a transient receptor potential (TRP) protein.
Experimental approach: Macroscopic and single channel currents were recorded from transfected HEK293 cells by patch-clamp techniques.
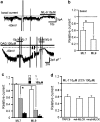
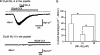
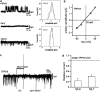
Key results: Cationic currents elicited by carbachol (CCh; 100 microM) in HEK293 cells overexpressing murine TRPC6 (I(TRPC6)) were dose-dependently inhibited by externally applied ML-9 (IC(50)=7.8 microM). This inhibition was voltage-dependent and occurred as fast as external Na(+) removal. Another MLCK inhibitor, wortmannin (3 microM), and MLCK inhibitory peptides MLCK-IP(11-19) (10 microM) and -IP(480-501) (1 microM) showed little effects on I(TRPC6) density and the inhibitory efficacy of ML-9. The extent of the inhibition also unchanged with co-expression of wild-type or a dominant negative mutant of MLCK. Inhibitory effects of ML-9 on I(TRPC6) remained unaffected whether TRPC6 was activated constitutively or by a diacylglycerol analogue OAG (100 microM). Similar rapid inhibition was also observed with a ML-9 relative, ML-7. Intracellular perfusion of ML-9 via patch pipette, dose-dependently suppressed I(TRPC6). In inside-out patch configuration, bath application of ML-9 (and ML-7) rapidly diminished approximately 35pS single TRPC6 channel activities. Contrarily, currents due to TRPC7 expression were rapidly enhanced by externally applied ML-9 and ML-7, which was not prevented by MLCK inhibitory peptides.
Conclusion and implications: These results strongly suggest that ML compounds inhibit TRPC6 channels via a mechanism independent of inhibition of MLCK activity.
Figures
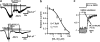

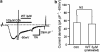
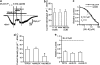

Similar articles
-
Multiple regulation by calcium of murine homologues of transient receptor potential proteins TRPC6 and TRPC7 expressed in HEK293 cells.J Physiol. 2004 Dec 1;561(Pt 2):415-32. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.075051. Epub 2004 Oct 7. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15579537 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase is essential for activation of TRPC5 channels expressed in HEK293 cells.J Physiol. 2006 Jan 15;570(Pt 2):219-35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.097998. Epub 2005 Nov 10. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16284075 Free PMC article.
-
Role of calmodulin and myosin light chain kinase in the activation of carbachol-activated cationic current in murine ileal myocytes.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007 Dec;85(12):1254-62. doi: 10.1139/Y07-118. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 18066127
-
TRPC6: physiological function and pathophysiological relevance.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;222:157-88. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-54215-2_7. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24756706 Review.
-
Transient receptor potential canonical 7: a diacylglycerol-activated non-selective cation channel.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;222:189-204. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-54215-2_8. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24756707 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential effects of myosin light chain kinase inhibition on contractility, force development and myosin light chain 20 phosphorylation of rat cervical and thoracic duct lymphatics.J Physiol. 2011 Nov 15;589(Pt 22):5415-29. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.218446. Epub 2011 Sep 19. J Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21930597 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological modulation of diacylglycerol-sensitive TRPC3/6/7 channels.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011 Jan 1;12(1):35-41. doi: 10.2174/138920111793937943. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 20932261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heart failure switches the RV alpha1-adrenergic inotropic response from negative to positive.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Mar;298(3):H913-20. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00259.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 24. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20035030 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of calcium channels in smooth muscle: new insights into the role of myosin light chain kinase.Channels (Austin). 2014;8(5):402-13. doi: 10.4161/19336950.2014.950537. Channels (Austin). 2014. PMID: 25483583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Rheological Properties of Healthy versus Dupuytren Fibroblasts When Treated with a Cell Contraction Inhibitor by Atomic Force Microscope.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 20;24(3):2043. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032043. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akar F, Jiang G, Paul RJ, O'Neill WC. Contractile regulation of the Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransporter in vascular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001;281:C579–C584. - PubMed
-
- Burdyga TV, Wray S. The effect of inhibition myosin light chain kinase by wortmannin on intracellular Ca2+, electrical activity and force in phasic smooth muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1998;436:801–803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

