Post-ischemic treatment with erythropoietin or carbamylated erythropoietin reduces infarction and improves neurological outcome in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 17603558
- PMCID: PMC2189829
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707285
Post-ischemic treatment with erythropoietin or carbamylated erythropoietin reduces infarction and improves neurological outcome in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia
Abstract
Background and purpose: Recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEPO; Epoetin-alpha; PROCRITtrade mark) has been shown to exert neuroprotective and restorative effects in a variety of CNS injury models. However, limited information is available regarding the dose levels required for these beneficial effects or the neuronal responses that may underlie them. Here we have investigated the dose-response to rhEPO and compared the effects of rhEPO with those of carbamylated rhEPO (CEPO) in a model of cerebral stroke in rats.
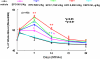
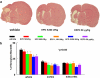
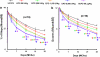
Experimental approach: Rats subjected to embolic middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo) were treated with rhEPO or CEPO, starting at 6 h and repeated at 24 and 48 h, after MCAo. Cerebral infarct volumes were assessed at 28 days and neurological impairment at 7, 14, 21 and 28 days, post-MCAo.
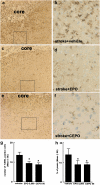
Key results: rhEPO at dose levels of 500, 1150 or 5000 IU kg(-1) or CEPO at a dose level of 50 microg kg(-1) significantly reduced cortical infarct volume and reduced neurologic impairment. All doses of rhEPO, but not CEPO, produced a transient increase in haematocrit, while rhEPO and CEPO substantially reduced the number of apoptotic cells and activated microglia in the ischemic boundary region.
Conclusions and implications: These data indicate that rhEPO and CEPO have anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects, even with administration at 6 h following embolic MCAo in rats. Taken together, these actions of rhEPO and CEPO are likely to contribute to their reduction of neurologic impairment following cerebral ischemia.
Figures
Comment in
-
Neuroprotection with or without erythropoiesis; sometimes less is more.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Aug;151(8):1141-2. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707287. Epub 2007 May 29. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17533424 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of erythropoietin pretreatment in a rodent model of transient middle cerebral artery occlusion.J Neurosurg. 2014 Jul;121(1):55-62. doi: 10.3171/2014.2.JNS132197. Epub 2014 Apr 4. J Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 24702327
-
Carbamylated erythropoietin is neuroprotective in an experimental model of traumatic brain injury.Crit Care Med. 2008 Mar;36(3):975-8. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0B013E3181644343. Crit Care Med. 2008. PMID: 18176311
-
Intranasal recombinant human erythropoietin protects rats against focal cerebral ischemia.Neurosci Lett. 2005 Oct 14;387(1):5-10. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2005.07.008. Neurosci Lett. 2005. PMID: 16054296
-
Carbamylated erythropoietin to treat neuronal injury: new development strategies.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008 Aug;17(8):1175-86. doi: 10.1517/13543784.17.8.1175. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18616414 Review.
-
Neuroprotective properties of epoetin alfa.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2002;17 Suppl 1:8-12. doi: 10.1093/ndt/17.suppl_1.8. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2002. PMID: 11812906 Review.
Cited by
-
Erythropoietin in the critically ill: do we ask the right questions?Crit Care. 2012 Sep 26;16(5):319. doi: 10.1186/cc11430. Crit Care. 2012. PMID: 23016869 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological approaches to acute ischaemic stroke: reperfusion certainly, neuroprotection possibly.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Mar;153 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S325-38. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707594. Epub 2007 Dec 3. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18059324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Erythropoietin and Its Derivatives on Ischemic Stroke Therapy: A Comprehensive Review.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 17;13:743926. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.743926. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35250554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancement of ventricular-subventricular zone-derived neurogenesis and oligodendrogenesis by erythropoietin and its derivatives.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Nov 27;7:235. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00235. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24348331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic effects of syringaldehyde on spinal cord ischemia in rabbits.Saudi Med J. 2020 Apr;41(4):341-350. doi: 10.15537/smj.2020.4.24993. Saudi Med J. 2020. PMID: 32291420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agnello D, Bigini P, Villa P, Mennini T, Cerami A, Brines ML, et al. Erythropoietin exerts an anti-inflammatory effect on the CNS in a model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain Res. 2002;952:128–134. - PubMed
-
- Belayev L, Khoutorova L, Zhao W, Vigdorchik A, Belayev A, Busto R, et al. Neuroprotective effect of darbepoetin alfa, a novel recombinant erythropoietic protein, in focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke. 2005;36:1071–1076. - PubMed
-
- Bernaudin M, Marti HH, Roussel S, Divoux D, Nouvelot A, MacKenzie ET, et al. A potential role for erythropoietin in focal permanent cerebral ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1999;19:643–651. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

