Mechanistic studies of the long chain acyl-CoA synthetase Faa1p from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 17604220
- PMCID: PMC2223485
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2007.05.009
Mechanistic studies of the long chain acyl-CoA synthetase Faa1p from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
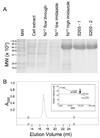
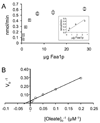
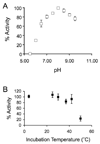
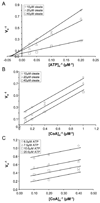
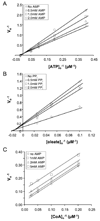
Long chain acyl-CoA synthetase (ACSL; fatty acid CoA ligase: AMP forming; EC 6.2.1.3) catalyzes the formation of acyl-CoA through a process, which requires fatty acid, ATP and coenzymeA as substrates. In the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae the principal ACSL is Faa1p (encoded by the FAA1 gene). The preferred substrates for this enzyme are cis-monounsaturated long chain fatty acids. Our previous work has shown Faa1p is a principal component of a fatty acid transport/activation complex that also includes the fatty acid transport protein Fat1p. In the present work hexameric histidine tagged Faa1p was purified to homogeneity through a two-step process in the presence of 0.1% eta-dodecyl-beta-maltoside following expression at 15 degrees C in Escherichia coli. In order to further define the role of this enzyme in fatty acid transport-coupled activation (vectorial acylation), initial velocity kinetic studies were completed to define the kinetic parameters of Faa1p in response to the different substrates and to define mechanism. These studies showed Faa1p had a Vmax of 158.2 nmol/min/mg protein and a Km of 71.1 microM oleate. When the concentration of oleate was held constant at 50 microM, the Km for CoA and ATP were 18.3 microM and 51.6 microM respectively. These initial velocity studies demonstrated the enzyme mechanism for Faa1p was Bi Uni Uni Bi Ping Pong.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vectorial acylation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Fat1p and fatty acyl-CoA synthetase are interacting components of a fatty acid import complex.J Biol Chem. 2003 May 2;278(18):16414-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M210557200. Epub 2003 Feb 24. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12601005
-
Biochemical studies of three Saccharomyces cerevisiae acyl-CoA synthetases, Faa1p, Faa2p, and Faa3p.J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 10;269(23):16348-56. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 8206942
-
The Acyl-CoA synthetases encoded within FAA1 and FAA4 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae function as components of the fatty acid transport system linking import, activation, and intracellular Utilization.J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 5;276(40):37051-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100884200. Epub 2001 Jul 27. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11477098
-
Yeast acyl-CoA synthetases at the crossroads of fatty acid metabolism and regulation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Mar;1771(3):286-98. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2006.05.003. Epub 2006 May 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 16798075 Review.
-
Long-chain fatty acid transport in bacteria and yeast. Paradigms for defining the mechanism underlying this protein-mediated process.Mol Cell Biochem. 1999 Feb;192(1-2):41-52. Mol Cell Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10331657 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a (CPT1a) is part of an outer membrane fatty acid transfer complex.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 22;286(29):25655-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.228692. Epub 2011 May 26. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21622568 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational dynamics in the Acyl-CoA synthetases, adenylation domains of non-ribosomal peptide synthetases, and firefly luciferase.ACS Chem Biol. 2009 Oct 16;4(10):811-27. doi: 10.1021/cb900156h. ACS Chem Biol. 2009. PMID: 19610673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 2 is involved in seed oil production in Brassica napus.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Jan 13;20(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-2240-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 31931712 Free PMC article.
-
Key enzymes involved in the utilization of fatty acids by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a review.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 11;14:1294182. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1294182. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38274755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Carboxylic Acid Reductases as Enzymes in the Toolbox for Synthetic Chemistry.ChemCatChem. 2017 Mar 20;9(6):1005-1017. doi: 10.1002/cctc.201601249. Epub 2017 Feb 14. ChemCatChem. 2017. PMID: 28450969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tong F, Black PN, Coleman RA, DiRusso CC. Fatty acid transport by vectorial acylation in mammals: Roles played by different isoforms of rat long-chain acyl-CoA synthetases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2006 - PubMed
-
- Mashek DG, McKenzie MA, Van Horn CG, Coleman RA. Rat long chain acyl-CoA synthetase 5 increases fatty acid uptake and partitioning to cellular triacylglycerol in McArdle-RH7777 cells. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:945–950. - PubMed
-
- Faergeman NJ, Black PN, Zhao XD, Knudsen J, DiRusso CC. The Acyl-CoA synthetases encoded within FAA1 and FAA4 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae function as components of the fatty acid transport system linking import, activation, and intracellular Utilization. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:37051–37059. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

