Machine learning and its applications to biology
- PMID: 17604446
- PMCID: PMC1904382
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030116
Machine learning and its applications to biology
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
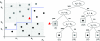


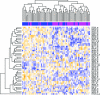

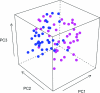

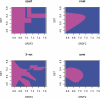
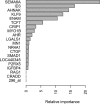
References
-
- Rosenblatt F. The perceptron: A probabilistic model for information storage and organization in the brain. Psychol Rev. 1958;65:386–408. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter GA, Grossberg S. The art of adaptive pattern recognition by a self-organizing neural network. Computer. 1988;21:77–88.
-
- Fukushima K. Neocognitron: A self-organizing neural network model for a mechanism of pattern recognition unaffected by shift in position. Biol Cybern. 1980;36:193–202. - PubMed
-
- Weston J, Leslie C, Ie E, Zhou D, Elisseeff A, et al. Semi-supervised protein classification using cluster kernels. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:3241–3247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 1 P41 HG004059/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA100740/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 2P30 CA022453-24/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R21EB000990-03/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 1R21CA100740-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB000990/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR017708/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41 HG004059/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA117478/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS045207/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA022453/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01CA117478-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG003491/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR17708/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01NS045207-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01HG003491-01A1/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

