Nature, decay, and spiraling of the effects of fear-inducing arguments and HIV counseling and testing: a meta-analysis of the short- and long-term outcomes of HIV-prevention interventions
- PMID: 17605570
- PMCID: PMC2703734
- DOI: 10.1037/0278-6133.26.4.496
Nature, decay, and spiraling of the effects of fear-inducing arguments and HIV counseling and testing: a meta-analysis of the short- and long-term outcomes of HIV-prevention interventions
Erratum in
- Health Psychol. 2007 Nov;26(6):815-6
Abstract
Objective: To examine the long-term efficacy of both fear-inducing arguments and HIV counseling and testing at encouraging and maintaining knowledge about HIV transmission and prevention, as well as condom use.
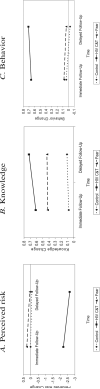
Design: Analyses were conducted with a sample of 150 treatment groups and 34 controls and included measures of change at an immediate follow-up and a delayed follow-up.
Main outcome measures: The main outcome measures were perceived risk of HIV infection, knowledge about HIV, and condom use.
Results: Results indicated that receiving fear-inducing arguments increased perceptions of risk at the immediate follow-up but decreased knowledge and condom use, whereas resolving fear via HIV counseling and testing decreased perceptions of risk and increased knowledge and condom use at both the immediate and delayed follow-ups. The effects on perceived risk [corrected] decreased over time, but the effects on knowledge [corrected] condom use became more pronounced.
Conclusion: Inducing fear is not an effective way to promote HIV-relevant learning or condom use either immediately following the intervention or later on. However, HIV counseling and testing can provide an outlet for HIV-related anxiety and, subsequently, gains in both knowledge and behavior change immediately and longitudinally.
Copyright 2007 APA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An assessment of brief group interventions to increase condom use by heterosexual crack smokers living with HIV infection.AIDS Care. 2012;24(2):220-31. doi: 10.1080/09540121.2011.597707. Epub 2011 Jul 25. AIDS Care. 2012. PMID: 21780981 Clinical Trial.
-
Outcomes of an AIDS prevention program for methadone patients.Int J Addict. 1991 Jun;26(6):629-55. doi: 10.3109/10826089109058910. Int J Addict. 1991. PMID: 1757169
-
On the Efficacy and Mediation of a One-on-One HIV Risk-Reduction Intervention for African American Men Who Have Sex with Men: A Randomized Controlled Trial.AIDS Behav. 2015 Jul;19(7):1247-62. doi: 10.1007/s10461-014-0961-2. AIDS Behav. 2015. PMID: 25449552 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sexual behaviour change following HIV testing services: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Int AIDS Soc. 2020 Nov;23(11):e25635. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25635. J Int AIDS Soc. 2020. PMID: 33161636 Free PMC article.
-
How can psychological theory help to promote condom use in sub-Saharan African developing countries?J R Soc Health. 1997 Jun;117(3):186-91. doi: 10.1177/146642409711700311. J R Soc Health. 1997. PMID: 9195835 Review.
Cited by
-
What's Next in Design for Global Health? How Design and Global Health Must Adapt for a Preferable Future.Glob Health Sci Pract. 2021 Nov 29;9(Suppl 2):S283-S294. doi: 10.9745/GHSP-D-21-00280. Print 2021 Nov 29. Glob Health Sci Pract. 2021. PMID: 34845051 Free PMC article.
-
Functional brain imaging predicts public health campaign success.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016 Feb;11(2):204-14. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsv108. Epub 2015 Sep 23. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26400858 Free PMC article.
-
HIV Voluntary Counseling and Testing (VCT-HIV) effectiveness for sexual risk-reduction among key populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis.EClinicalMedicine. 2022 Aug 12;52:101612. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101612. eCollection 2022 Oct. EClinicalMedicine. 2022. PMID: 36034408 Free PMC article.
-
Threat appeals in health communication: messages that elicit fear and enhance perceived efficacy positively impact on young male drivers.BMC Public Health. 2016 Jul 27;16:645. doi: 10.1186/s12889-016-3227-2. BMC Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27460475 Free PMC article.
-
An Assessment of Behavior Change Techniques in Two Versions of a Dietary Mobile Application: The Change4Life Food Scanner.Front Public Health. 2022 Feb 23;10:803152. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.803152. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35284376 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albarracín D. Unrealistic expectations: The ironic effects of expectancy disconfirmation in persuasion. In: Chadee D, Young JR, editors. Current themes and perspectives in social psychology. University of the West Indies Press; Trinidad: (in press)