Extra-embryonic endoderm cells derived from ES cells induced by GATA factors acquire the character of XEN cells
- PMID: 17605826
- PMCID: PMC1933422
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-213X-7-80
Extra-embryonic endoderm cells derived from ES cells induced by GATA factors acquire the character of XEN cells
Abstract
Background: Three types of cell lines have been established from mouse blastocysts: embryonic stem (ES) cells, trophoblast stem (TS) cells, and extra-embryonic endoderm (XEN) cells, which have the potential to differentiate into their respective cognate lineages. ES cells can differentiate in vitro not only into somatic cell lineages but into extra-embryonic lineages, including trophectoderm and extra-embryonic endoderm (ExEn) as well. TS cells can be established from ES cells by the artificial repression of Oct3/4 or the upregulation of Cdx2 in the presence of FGF4 on feeder cells. The relationship between these embryo-derived XEN cells and ES cell-derived ExEn cell lines remains unclear, although we have previously reported that overexpression of Gata4 or Gata6 induces differentiation of mouse ES cells into extra-embryonic endoderm in vitro.
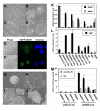
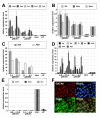
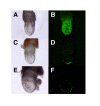
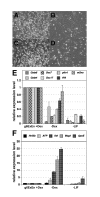
Results: A system in which GATA factors were conditionally activated revealed that the cells continue to proliferate while expressing a set of extra-embryonic endoderm markers, and, following injection into blastocysts, contribute only to the extra-embryonic endoderm lineage in vivo. Although the in vivo contribution is limited to cells of parietal endoderm lineage, Gata-induced extra-embryonic endoderm cells (gExEn) can be induced to differentiate into visceral endoderm-like cells in vitro by repression of Gata6. During early passage, the propagation of gExEn cells is dependent on the expression of the Gata6 transgene. These cells, however, lose this dependency following establishment of endogenous Gata6 expression.
Conclusion: We show here that Gata-induced extra-embryonic endoderm cells derived from ES cells mimic the character of XEN cells. These findings indicate that Gata transcription factors are sufficient for the derivation and propagation of XEN-like extra-embryonic endoderm cells from ES cells.
Figures

References
-
- Enders AC, Schlafke S. Comparative aspects of blastocyst-endometrial interactions at implantation. Ciba Found Symp. 1978:3–32. - PubMed
-
- Koutsourakis M, Langeveld A, Patient R, Beddington R, Grosveld F. The transcription factor GATA6 is essential for early extraembryonic development. Development. 1999;126:723–732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

