Modulatory effects of nitric oxide-active drugs on the anticonvulsant activity of lamotrigine in an experimental model of partial complex epilepsy in the rat
- PMID: 17605830
- PMCID: PMC1950521
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-8-47
Modulatory effects of nitric oxide-active drugs on the anticonvulsant activity of lamotrigine in an experimental model of partial complex epilepsy in the rat
Abstract
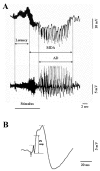
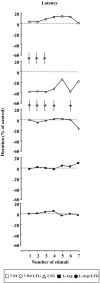
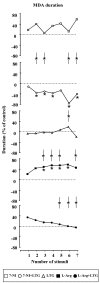
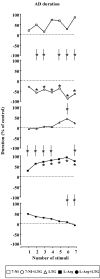
Background: The effects induced by administering the anticonvulsant lamotrigine, the preferential inhibitor of neuronal nitric oxide synthase 7-nitroindazole and the precursor of NO synthesis L-arginine, alone or in combination, on an experimental model of partial complex seizures (maximal dentate gyrus activation) were studied in urethane anaesthetized rats. The epileptic activity of the dentate gyrus was obtained through the repetitive stimulation of the angular bundle and maximal dentate gyrus activation latency, duration and post-stimulus afterdischarge duration were evaluated.
Results: Either Lamotrigine (10 mg kg-1) or 7-nitroindazole (75 mg kg-1) i.p. administration had an anticonvulsant effect, significantly reducing the number of animals responding to angular bundle stimulation. On the contrary, i.p. injection of L-arginine (1 g kg-1) induced an aggravation of the epileptiform phenomena, demonstrated by the significant augmentation of the duration of both maximal dentate activation and afterdischarge. Furthermore, the injection of lamotrigine and 7-nitroindazole in combination significantly increased the anticonvulsant effects induced by the same drugs separately, either reducing the number of responding animals or decreasing both maximal dentate gyrus activation and afterdischarge durations. On the contrary, the combined treatment with L-arginine and lamotrigine did not modify the maximal dentate gyrus activation parameters suggesting an adversative effect of L-arginine-increased nitric oxide levels on the lamotrigine-induced anticonvulsant action.
Conclusion: The present results indicate that the nitrergic neurotransmission exerts a significant modulatory role in the control of the development of paroxystic phenomena in the maximal dentate gyrus activation model of epilepsy. Finally, our data suggest a functional relationship between the nitric oxide system and the anticonvulsant effect of lamotrigine which could be enhanced by reducing nitric oxide levels and, conversely, dampened by an increased nitrergic activity.
Figures
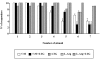
Similar articles
-
In the rat maximal dentate activation model of partial complex epilepsy, the anticonvulsant activity of levetiracetam is modulated by nitric oxide-active drugs.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2009 Jul;116(7):831-9. doi: 10.1007/s00702-009-0233-x. Epub 2009 May 12. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2009. PMID: 19533294
-
Lamotrigine differently modulates 7-nitroindazole and L-arginine influence on rat maximal dentate gyrus activation.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2008;115(1):27-34. doi: 10.1007/s00702-007-0824-3. Epub 2007 Nov 12. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2008. PMID: 17994188
-
Cholecystokinin-8 sulfate modulates the anticonvulsant efficacy of vigabatrin in an experimental model of partial complex epilepsy in the rat.Epilepsia. 2009 Apr;50(4):721-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01956.x. Epub 2009 Feb 12. Epilepsia. 2009. PMID: 19220409
-
Nitric oxide, epileptic seizures, and action of antiepileptic drugs.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2011 Nov;10(7):808-19. doi: 10.2174/187152711798072347. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21999730 Review.
-
Is nitric oxide involved in the anticonvulsant action of antiepileptic drugs?Pol J Pharmacol. 2003 Jul-Aug;55(4):535-42. Pol J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14581711 Review.
Cited by
-
Short-Term Amygdala Low-Frequency Stimulation Does not Influence Hippocampal Interneuron Changes Observed in the Pilocarpine Model of Epilepsy.Cells. 2021 Mar 1;10(3):520. doi: 10.3390/cells10030520. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33804543 Free PMC article.
-
In the rat maximal dentate activation model of partial complex epilepsy, the anticonvulsant activity of levetiracetam is modulated by nitric oxide-active drugs.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2009 Jul;116(7):831-9. doi: 10.1007/s00702-009-0233-x. Epub 2009 May 12. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2009. PMID: 19533294
-
Nitric oxide regulates activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP) in the dentate gyrus of the rodent model of kainic acid-induced seizure.J Mol Neurosci. 2009 Sep;39(1-2):9-21. doi: 10.1007/s12031-008-9169-0. Epub 2009 Jan 7. J Mol Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19130308
-
Glial source of nitric oxide in epileptogenesis: A target for disease modification in epilepsy.J Neurosci Res. 2019 Nov;97(11):1363-1377. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24205. Epub 2017 Dec 12. J Neurosci Res. 2019. PMID: 29230865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress in Patients with Drug Resistant Partial Complex Seizure.Behav Sci (Basel). 2018 Jun 9;8(6):59. doi: 10.3390/bs8060059. Behav Sci (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29890748 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Przegalinski E, Baran L, Siwanowicz The role of nitric oxide in chemically- and electrically-induced seizures in mice. Neurosci Lett. 1996;217:145–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

