Differential engagement of Tim-1 during activation can positively or negatively costimulate T cell expansion and effector function
- PMID: 17606630
- PMCID: PMC2118637
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20062498
Differential engagement of Tim-1 during activation can positively or negatively costimulate T cell expansion and effector function
Abstract
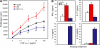
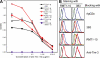
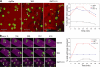
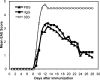
It has been suggested that T cell immunoglobulin mucin (Tim)-1 expressed on T cells serves to positively costimulate T cell responses. However, crosslinking of Tim-1 by its ligand Tim-4 resulted in either activation or inhibition of T cell responses, thus raising the issue of whether Tim-1 can have a dual function as a costimulator. To resolve this issue, we tested a series of monoclonal antibodies specific for Tim-1 and identified two antibodies that showed opposite functional effects. One anti-Tim-1 antibody increased the frequency of antigen-specific T cells, the production of the proinflammatory cytokines IFN-gamma and IL-17, and the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. In contrast, another anti-Tim-1 antibody inhibited the generation of antigen-specific T cells, production of IFN-gamma and IL-17, and development of autoimmunity, and it caused a strong Th2 response. Both antibodies bound to closely related epitopes in the IgV domain of the Tim-1 molecule, but the activating antibody had an avidity for Tim-1 that was 17 times higher than the inhibitory antibody. Although both anti-Tim-1 antibodies induced CD3 capping, only the activating antibody caused strong cytoskeletal reorganization and motility. These data indicate that Tim-1 regulates T cell responses and that Tim-1 engagement can alter T cell function depending on the affinity/avidity with which it is engaged.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tim-1 stimulation of dendritic cells regulates the balance between effector and regulatory T cells.Eur J Immunol. 2011 Jun;41(6):1539-49. doi: 10.1002/eji.201040993. Epub 2011 May 25. Eur J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21469101 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination with cell immunoglobulin mucin-1 antibodies and inactivated influenza enhances vaccine-specific lymphocyte proliferation, interferon-gamma production and cross-strain reactivity.Clin Exp Immunol. 2006 Jul;145(1):123-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03107.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16792682 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous Tim-1 (Kim-1) promotes T-cell responses and cell-mediated injury in experimental crescentic glomerulonephritis.Kidney Int. 2012 May;81(9):844-55. doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.424. Epub 2011 Dec 28. Kidney Int. 2012. PMID: 22205357
-
The role of the T-cell costimulatory molecule Tim-1 in the immune response.Immunol Res. 2007;39(1-3):52-61. doi: 10.1007/s12026-007-0063-6. Immunol Res. 2007. PMID: 17917055 Review.
-
The TIM gene family regulates autoimmune and allergic diseases.Trends Mol Med. 2005 Aug;11(8):362-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2005.06.008. Trends Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 16002337 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting TIM-1 on CD4 T cells depresses macrophage activation and overcomes ischemia-reperfusion injury in mouse orthotopic liver transplantation.Am J Transplant. 2013 Jan;13(1):56-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04316.x. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Am J Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23137033 Free PMC article.
-
TIM-3: a novel regulatory molecule of alloimmune activation.J Immunol. 2010 Nov 15;185(10):5806-19. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903435. Epub 2010 Oct 18. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20956339 Free PMC article.
-
Tim-1 signaling substitutes for conventional signal 1 and requires costimulation to induce T cell proliferation.J Immunol. 2009 Feb 1;182(3):1379-85. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.182.3.1379. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19155484 Free PMC article.
-
TIM-4 expressed on APCs induces T cell expansion and survival.J Immunol. 2008 Apr 1;180(7):4706-13. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.7.4706. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18354194 Free PMC article.
-
HAVCR1 gene haplotypes and infection by different viral hepatitis C virus genotypes.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012 Feb;19(2):223-7. doi: 10.1128/CVI.05305-11. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22190394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meyers, J.H., C.A. Sabatos, S. Chakravarti, and V.K. Kuchroo. 2005. The TIM gene family regulates autoimmune and allergic diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 11:362–369. - PubMed
-
- Kuchroo, V.K., D.T. Umetsu, R.H. DeKruyff, and G.J. Freeman. 2003. The TIM gene family: emerging roles in immunity and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3:454–462. - PubMed
-
- Ichimura, T., J.V. Bonventre, V. Bailly, H. Wei, C.A. Hession, R.L. Cate, and M. Sanicola. 1998. Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), a putative epithelial cell adhesion molecule containing a novel immunoglobulin domain, is up-regulated in renal cells after injury. J. Biol. Chem. 273:4135–4142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS 30843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AI 586080/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- NS 045593/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK090105/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI 44880/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI041521/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI070820/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI044880/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS030843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R29 NS030843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS038037/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS030843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI058680/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI 139761/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI 41521/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI139671/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI044880/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS035685/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI058680/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- NS 046414/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS046414/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS 35685/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

