In vivo efficacy of a novel oxazolidinone compound in two mouse models of infection
- PMID: 17606686
- PMCID: PMC2043186
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01567-06
In vivo efficacy of a novel oxazolidinone compound in two mouse models of infection
Abstract
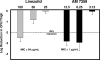
A novel oxazolidinone, AM 7359, was evaluated in two mouse models of Staphylococcus aureus infection. AM 7359 and linezolid were equally efficacious in a methicillin-susceptible S. aureus organ burden model and a methicillin-resistant S. aureus localized infection model. However, AM 7359 was eightfold more efficacious than linezolid against a linezolid- and methicillin-resistant S. aureus strain in this localized (thigh) infection model.
Figures
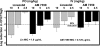
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of linezolid in treatment of experimental endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001 Aug;45(8):2304-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.8.2304-2308.2001. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001. PMID: 11451689 Free PMC article.
-
Linezolid to decrease length of stay in the hospital for patients with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection.Clin Infect Dis. 2003 Jan 1;36(1):124; author reply 124-5. doi: 10.1086/345300. Clin Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 12491215 No abstract available.
-
In vivo efficacy of ceftaroline (PPI-0903), a new broad-spectrum cephalosporin, compared with linezolid and vancomycin against methicillin-resistant and vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus in a rabbit endocarditis model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Sep;51(9):3397-400. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01242-06. Epub 2007 Jun 25. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17591849 Free PMC article.
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) endocarditis treated with linezolid.Scand J Infect Dis. 2008;40(1):67-73. doi: 10.1080/00365540701509915. Epub 2007 Jul 27. Scand J Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 17852941 Review.
-
The importance of tissue penetration in achieving successful antimicrobial treatment of nosocomial pneumonia and complicated skin and soft-tissue infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: vancomycin and linezolid.Curr Med Res Opin. 2010 Mar;26(3):571-88. doi: 10.1185/03007990903512057. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010. PMID: 20055750 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemical Genetic Analysis and Functional Characterization of Staphylococcal Wall Teichoic Acid 2-Epimerases Reveals Unconventional Antibiotic Drug Targets.PLoS Pathog. 2016 May 4;12(5):e1005585. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005585. eCollection 2016 May. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27144276 Free PMC article.
-
Host gene expression profiling and in vivo cytokine studies to characterize the role of linezolid and vancomycin in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) murine sepsis model.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60463. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060463. Epub 2013 Apr 2. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23565251 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo activity of ceftobiprole in murine skin infections due to Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Jan;54(1):116-25. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00642-09. Epub 2009 Nov 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 19884364 Free PMC article.
-
Linezolid Exerts Greater Bacterial Clearance but No Modification of Host Lung Gene Expression Profiling: A Mouse MRSA Pneumonia Model.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 27;8(6):e67994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067994. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23826353 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of wall teichoic acid inhibitors as potential anti-MRSA β-lactam combination agents.Chem Biol. 2013 Feb 21;20(2):272-84. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2012.11.013. Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23438756 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attassi, K., E. Hershberger, R. Alam, and M. J. Zervos. 2002. Thrombocytopenia associated with linezolid therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 34:695-698. - PubMed
-
- Auckland, C., L. Teare, F. Cooke, M. E. Kaufman, M. Warner, G. Jones, K. Bamford, H. Ayles, and A. P. Johnson. 2002. Linezolid-resistant enterococci: report of the first isolates in the United Kingdom. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 50:743-746. - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2000. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically, 5th ed. Approved standard M7-45(20). Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA.
-
- Craig, W. A. 1996. Antimicrobial resistance issues of the future. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 25:213-217. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

