Insights into the mechanism of FTY720 and compatibility with regulatory T cells for the inhibition of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)
- PMID: 17606761
- PMCID: PMC2200903
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-05-087940
Insights into the mechanism of FTY720 and compatibility with regulatory T cells for the inhibition of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)
Abstract
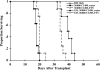
The immunomodulator FTY720 (FTY) has been shown to be beneficial in experimental models of organ transplantation and autoimmunity. We show that FTY significantly inhibited but did not prevent graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) in lethally irradiated or nonirradiated allogeneic recipients. Although most studies implicate prevention of lymphocyte egress from lymphoid organs as the primary mechanism of action, our data indicate that FTY effects on the host are more likely to be responsible for GVHD inhibition. FTY reduced splenic CD11c+ cells by 50%, and similarly reduced CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responder frequencies in the spleen early after transplantation. Imaging of GFP+ effectors indicated that FTY modified donor effector T-cell migration to secondary lymphoid organs, but did not uniformly trap T cells in lymph nodes or prevent early effector migration to GVHD parenchymal target organs. Administration of FTY only prior to transplantation inhibited GVHD, indicating that the primary function of FTY may be targeted to host cells. FTY was additive with regulatory T cells for GVHD inhibition. FTY slightly impaired but did not abrogate a graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) effect against C1498, a myeloid leukemia. Our data further define the mechanisms of action and provide insight as to the potential clinical uses of FTY in allogeneic bone marrow transplant recipients.
Figures
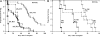



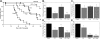

References
-
- Brinkmann V. FTY720: mechanism of action and potential benefit in organ transplantation. Yonsei Med J. 2004;45:991–997. - PubMed
-
- Brinkmann V, Lynch KR. FTY720: targeting G-protein-coupled receptors for sphingosine 1-phosphate in transplantation and autoimmunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002;14:569–575. - PubMed
-
- Chiba K. FTY720, a new class of immunomodulator, inhibits lymphocyte egress from secondary lymphoid tissues and thymus by agonistic activity at sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 2005;108:308–319. - PubMed
-
- Yopp AC, Ledgerwood LG, Ochando JC, Bromberg JS. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulators: a new class of immunosuppressants. Clin Transplant. 2006;20:788–795. - PubMed
-
- Chiba K, Hoshino Y, Ohtsuki M, et al. Immunosuppressive activity of FTY720, sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor agonist, I: prevention of allograft rejection in rats and dogs by FTY720 and FTY720-phosphate. Transplant Proc. 2005;37:102–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

