Locally controlled inhibitory mechanisms are involved in eukaryotic GPCR-mediated chemosensing
- PMID: 17606871
- PMCID: PMC2064430
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200611096
Locally controlled inhibitory mechanisms are involved in eukaryotic GPCR-mediated chemosensing
Abstract
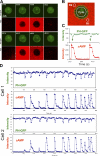
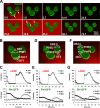
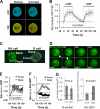
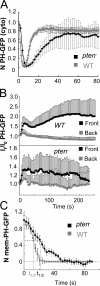
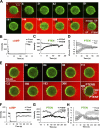
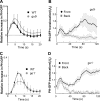
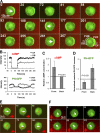
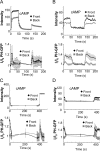
Gprotein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling mediates a balance of excitatory and inhibitory activities that regulate Dictyostelium chemosensing to cAMP. The molecular nature and kinetics of these inhibitors are unknown. We report that transient cAMP stimulations induce PIP3 responses without a refractory period, suggesting that GPCR-mediated inhibition accumulates and decays slowly. Moreover, exposure to cAMP gradients leads to asymmetric distribution of the inhibitory components. The gradients induce a stable accumulation of the PIP3 reporter PHCrac-GFP in the front of cells near the cAMP source. Rapid withdrawal of the gradient led to the reassociation of G protein subunits, and the return of the PIP3 phosphatase PTEN and PHCrac-GFP to their pre-stimulus distribution. Reapplication of cAMP stimulation produces a clear PHCrac-GFP translocation to the back but not to the front, indicating that a stronger inhibition is maintained in the front of a polarized cell. Our study demonstrates a novel spatiotemporal feature of currently unknown inhibitory mechanisms acting locally on the PI3K activation pathway.
Figures

References
-
- Arrieumerlou, C., and T. Meyer. 2005. A local coupling model and compass parameter for eukaryotic chemotaxis. Dev. Cell. 8:215–227. - PubMed
-
- Bominaar, A.A., and P.J. Van Haastert. 1993. Chemotactic antagonists of cAMP inhibit Dictyostelium phospholipase C. J. Cell Sci. 104:181–185. - PubMed
-
- Charest, P.G., and R.A. Firtel. 2006. Feedback signaling controls leading-edge formation during chemotaxis. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 16:339–347. - PubMed
-
- Chung, C.Y., S. Funamoto, and R.A. Firtel. 2001. a. Signaling pathways controlling cell polarity and chemotaxis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 26:557–566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

