Ozone and pulmonary innate immunity
- PMID: 17607006
- PMCID: PMC2647625
- DOI: 10.1513/pats.200701-023AW
Ozone and pulmonary innate immunity
Abstract
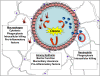
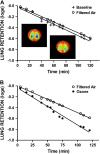
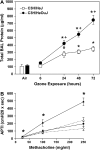
Ambient ozone (O(3)) is a commonly encountered environmental air pollutant with considerable impact on public health. Many other inhaled environmental toxicants can substantially affect pulmonary immune responses. Therefore, it is of considerable interest to better understand the complex interaction between environmental airway irritants and immunologically based human disease. The innate immune system represents the first line of defense against microbial pathogens. Intact innate immunity requires maintenance of an intact barrier to interface with the external environment, effective phagocytosis of microbial pathogens, and precise detection of pathogen-associated molecular patterns. We use ambient O(3) as a model to highlight the importance of understanding the role of exposure to ubiquitous air toxins and regulation of basic immune function. Inhalation of O(3) is associated with impaired antibacterial host defense, in part related to disruption of epithelial barrier and effective phagocytosis of pathogens. The functional response to ambient O(3) seems to be dependent on many components of the innate immune signaling. In this article, we review the complex interaction between inhalation of O(3) and pulmonary innate immunity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ambient ozone and pulmonary innate immunity.Immunol Res. 2011 Apr;49(1-3):173-91. doi: 10.1007/s12026-010-8180-z. Immunol Res. 2011. PMID: 21132467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Innate Immune System in Environmental Lung Diseases.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2021 May 10;21(5):34. doi: 10.1007/s11882-021-01011-0. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2021. PMID: 33970346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Individuals with increased inflammatory response to ozone demonstrate muted signaling of immune cell trafficking pathways.Respir Res. 2012 Oct 3;13(1):89. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-13-89. Respir Res. 2012. PMID: 23033980 Free PMC article.
-
The role of oxidative stress and innate immunity in O(3) and endotoxin-induced human allergic airway disease.Immunol Rev. 2011 Jul;242(1):91-105. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01035.x. Immunol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21682740 Review.
-
Epithelial and inflammatory responses in the airways of laboratory rats coexposed to ozone and biogenic substances: enhancement of toxicant-induced airway injury.Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2005 Jul;57 Suppl 1:129-41. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2005.05.013. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2005. PMID: 16092720 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of air pollutants on innate immunity: the role of Toll-like receptors and nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012 Jan;129(1):14-24; quiz 25-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.11.004. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22196521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of atmospheric pollutants on the Nrf2 survival pathway.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2010 Feb;17(2):369-82. doi: 10.1007/s11356-009-0140-6. Epub 2009 Apr 15. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2010. PMID: 19367423 Review.
-
Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress Study IV: ozone exposure of rats and its effect on antioxidants in plasma and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid.Free Radic Biol Med. 2011 Nov 1;51(9):1636-42. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.07.013. Epub 2011 Jul 22. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011. PMID: 21824516 Free PMC article.
-
Inhaled matters of the heart.Cardiovasc Regen Med. 2015;2:e997. doi: 10.14800/crm.997. Epub 2015 Sep 20. Cardiovasc Regen Med. 2015. PMID: 26665179 Free PMC article.
-
Geospatial Analysis of Environmental Atmospheric Risk Factors in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Nov 13;17(22):8414. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17228414. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33202965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dockery DW, Pope CA, Xu X, Spengler JD, Ware JH, Fay ME, Ferris BG, Speizer FE. An association between air pollution and mortality in six U.S. cities. N Engl J Med 1993;329:1754–1759. - PubMed
-
- Gryparis A, Forsberg B, Katsouyanni K, Analitis A, Touloumi G, Schwartz J, Samoli E, Medina S, Anderson HR, Niciu EM, et al. Acute effects of ozone on mortality from the “Air Pollution and Health: A European Approach” project. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004;28:28. - PubMed
-
- Katsouyanni K, Zmirou D, Spix C, Sunyer J, Schouten JP, Ponka A, Anderson HR, Le Moullec Y, Wojtyniak B, Vigotti MA, et al. Short-term effects of air pollution on health: a European approach using epidemiological time-series data. The APHEA project: background, objectives, design. Eur Respir J 1995;8:1030–1038. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
