Immunomodulatory roles of surfactant proteins A and D: implications in lung disease
- PMID: 17607008
- PMCID: PMC2647627
- DOI: 10.1513/pats.200701-018AW
Immunomodulatory roles of surfactant proteins A and D: implications in lung disease
Abstract
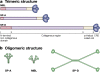
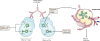
Surfactant, a lipoprotein complex, was originally described for its essential role in reducing surface tension at the air-liquid interface of the lung; however, it is now recognized as being a critical component in lung immune host defense. Surfactant proteins (SP)-A and -D are pattern recognition molecules of the collectin family of C-type lectins. SP-A and SP-D are part of the innate immune system and regulate the functions of other innate immune cells, such as macrophages. They also modulate the adaptive immune response by interacting with antigen-presenting cells and T cells, thereby linking innate and adaptive immunity. Emerging studies suggest that SP-A and SP-D function to modulate the immunologic environment of the lung so as to protect the host and, at the same time, modulate an overzealous inflammatory response that could potentially damage the lung and impair gas exchange. Numerous polymorphisms of SPs have been identified that may potentially possess differential functional abilities and may act via different receptors to ultimately alter the susceptibility to or severity of lung diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Nogee LM. Genetic mechanisms of surfactant deficiency. Biol Neonate 2004;85:314–318. - PubMed
-
- Wright JR. Immunoregulatory functions of surfactant proteins. Nat Rev Immunol 2005;5:58–68. - PubMed
-
- Stamme C, Walsh E, Wright JR. Surfactant protein A differentially regulates IFN-γ– and LPS-induced nitrite production by rat alveolar macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2000;23:772–779. - PubMed
-
- Ikegami M, Jobe AH, Whitsett J, Korfhagen T. Tolerance of SP-A–deficient mice to hyperoxia or exercise. J Appl Physiol 2000;89:644–648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
