Toxic cyanobacterial blooms in reservoirs under a semiarid mediterranean climate: the magnification of a problem
- PMID: 17607731
- PMCID: PMC3968935
- DOI: 10.1002/tox.20268
Toxic cyanobacterial blooms in reservoirs under a semiarid mediterranean climate: the magnification of a problem
Abstract
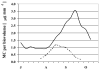
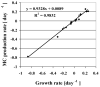
Sicilian reservoirs constitute the most important water resources available on the island. During summer 2001, the intense water utilization of Lake Arancio reservoir reduced the water level significantly, which coincided with the formation of intense blooms formed by the microcystin (MC)-producing cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. During summer 2003, Lake Arancio was continuously filled and the vertical stratification of the water column was maintained resulting in five to sixfold lower cell numbers of M. aeruginosa. For both years, a significant relationship between MC net production and Microcysytis cell growth was observed, implying that Microcystis cell numbers can be used to infer MC concentrations in water. Unexpectedly, dense blooms of the MC-producing cyanobacterium Planktothrix rubescens occurred during winter 2005/2006 in the reservoirs Lake Pozzillo, Prizzi, Nicoletti, and Garcia but have not been reported earlier. In this season, MC concentrations higher than those recorded in summer were measured, implying that monitoring of Mediterranean drinking water reservoirs needs to be intensified during winter, a season usually considered to be less prone to the formation of cyanobacterial blooms.
Figures

References
-
- Amé MV, Wunderlin DA. Effects of iron, ammonium and temperature on microcystin content by a concentrated Microcystis aeruginosa natural population. Water Air Soil Poll. 2005;168:235–248.
-
- Barbosa FAR, Padisák J. The forgotten lake stratification pattern: atelomixis, and its ecological importance. Verh int Verein Limnol. 2002;28:2381–2392.
-
- Briand JF, Jacquet S, Flinois C, Avois-Jacquet C, Maisonnette C, Leberre B, Humbert JF. Variations in the microcystin production of Planktothrix rubescens (cyanobacteria) assessed from a four-year survey of Lac du Bourget (France) and from laboratory experiments. Microb Ecol. 2005;50:418–428. - PubMed
-
- Chorus I, Bartram J. Toxic Cyanobacteria in water. E & FN Spon; London: 1999. p. 416.
-
- Chorus I, Niesel V, Fastner J, Wiedner C, Nixdorf B, Lindenschmidt K-E. Environmental factors and microcystin levels in water bodies. In: Chorus I, editor. Cyanotoxins. Occurrence, Causes, Consequences. Springer; Berlin: 2001. pp. 159–177.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

