Structural basis of PP2A inhibition by small t antigen
- PMID: 17608567
- PMCID: PMC1945078
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050202
Structural basis of PP2A inhibition by small t antigen
Abstract
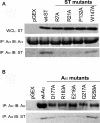
The SV40 small t antigen (ST) is a potent oncoprotein that perturbs the function of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A). ST directly interacts with the PP2A scaffolding A subunit and alters PP2A activity by displacing regulatory B subunits from the A subunit. We have determined the crystal structure of full-length ST in complex with PP2A A subunit at 3.1 A resolution. ST consists of an N-terminal J domain and a C-terminal unique domain that contains two zinc-binding motifs. Both the J domain and second zinc-binding motif interact with the intra-HEAT-repeat loops of HEAT repeats 3-7 of the A subunit, which overlaps with the binding site of the PP2A B56 subunit. Intriguingly, the first zinc-binding motif is in a position that may allow it to directly interact with and inhibit the phosphatase activity of the PP2A catalytic C subunit. These observations provide a structural basis for understanding the oncogenic functions of ST.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




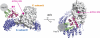

References
-
- Barbanti-Brodano G, Sabbioni S, Martini F, Negrini M, Corallini A, et al. Simian virus 40 infection in humans and association with human diseases: Results and hypotheses. Virology. 2004;318:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Skoczylas C, Fahrbach KM, Rundell K. Cellular targets of the SV40 small-t antigen in human cell transformation. Cell Cycle. 2004;3:606–610. - PubMed
-
- Rundell K, Parakati R. The role of the SV40 ST antigen in cell growth promotion and transformation. Semin Cancer Biol. 2001;11:5–13. - PubMed
-
- Yu J, Boyapati A, Rundell K. Critical role for SV40 small-t antigen in human cell transformation. Virology. 2001;290:192–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

