Human alpha2-macroglobulin is composed of multiple domains, as predicted by homology with complement component C3
- PMID: 17608619
- PMCID: PMC2267405
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20070764
Human alpha2-macroglobulin is composed of multiple domains, as predicted by homology with complement component C3
Abstract
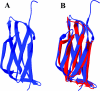
Human alpha2M (alpha2-macroglobulin) and the complement components C3 and C4 are thiol ester-containing proteins that evolved from the same ancestral gene. The recent structure determination of human C3 has allowed a detailed prediction of the location of domains within human alpha2M to be made. We describe here the expression and characterization of three alpha(2)M domains predicted to be involved in the stabilization of the thiol ester in native alpha2M and in its activation upon bait region proteolysis. The three newly expressed domains are MG2 (macroglobulin domain 2), TED (thiol ester-containing domain) and CUB (complement protein subcomponents C1r/C1s, urchin embryonic growth factor and bone morphogenetic protein 1) domain. Together with the previously characterized RBD (receptor-binding domain), they represent approx. 42% of the alpha2M polypeptide. Their expression as folded domains strongly supports the predicted domain organization of alpha2M. An X-ray crystal structure of MG2 shows it to have a fibronectin type-3 fold analogous to MG1-MG8 of C3. TED is, as predicted, an alpha-helical domain. CUB is a spliced domain composed of two stretches of polypeptide that flank TED in the primary structure. In intact C3 TED interacts with RBD, where it is in direct contact with the thiol ester, and with MG2 and CUB on opposite, flanking sides. In contrast, these alpha2M domains, as isolated species, show negligible interaction with one another, suggesting that the native conformation of alpha2M, and the consequent thiol ester-stabilizing domain-domain interactions, result from additional restraints imposed by the physical linkage of these domains or by additional domains in the protein.
Figures



References
-
- Sottrup-Jensen L. α-Macroglobulins. Structure, shape, and mechanism of proteinase complex formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1989;264:11539–11542. - PubMed
-
- Webb D. J., Crookston K. P., Hall S. W., Gonias S. L. Binding of transforming growth factor-β1 to immobilized human α2-macroglobulin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1992;292:487–492. - PubMed
-
- Ronne H., Anundi H., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Nerve growth factor binds to serum α2-macroglobulin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1979;87:330–336. - PubMed
-
- Gettins P., Cunningham L. W. Identification of 1H resonances from the bait region of human α2-macroglobulin and effects of proteases and methylamine. Biochemistry. 1986;25:5011–5017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

