Mechanism of multidrug recognition by MDR1/ABCB1
- PMID: 17608770
- PMCID: PMC11159003
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00538.x
Mechanism of multidrug recognition by MDR1/ABCB1
Abstract
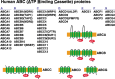
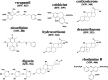
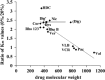
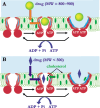
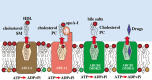
MDR1/ABCB1, a member of the ABC group of proteins, is clinically important because it is not only involved in multidrug resistance in cancer but also affects the pharmacokinetic properties of various drugs. The most puzzling feature of MDR1 is that it recognizes and transports such a wide variety of substrates. In the present review, the function of MDR1 is compared with that of other ABC proteins, particularly MDR2/ABCB4, to understand the mechanism of drug recognition and transport by MDR1. MDR2, the amino acid sequence of which has 86% similarity to that of MDR1, excretes phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol in the presence of bile salts. ABCA1 transfers phospholipids, preferentially phosphatidylcholine, and cholesterol to lipid-free apoA-I to generate pre-beta-HDL, and ABCG1 excretes phospholipids, preferentially sphingomyelin, and cholesterol. Cholesterol also binds directly to MDR1 and modulates substrate recognition by MDR1. Cholesterol may fill the empty space of the drug-binding site and aid the recognition of small drugs, and facilitates the ability of MDR1 to recognize compounds with various structures and molecular weights. Eukaryote ABC proteins may retain similar substrate binding pockets and move bound substrates in an ATP-dependent manner. The prototype of eukaryote ABC proteins might be those involved in membrane lipid transport.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Studies of human MDR1-MDR2 chimeras demonstrate the functional exchangeability of a major transmembrane segment of the multidrug transporter and phosphatidylcholine flippase.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Feb;19(2):1450-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.2.1450. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 9891078 Free PMC article.
-
Domain exchangeability between the multidrug transporter (MDR1) and phosphatidylcholine flippase (MDR2).Mol Pharmacol. 1999 Nov;56(5):997-1004. doi: 10.1124/mol.56.5.997. Mol Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10531406
-
Nuclear multidrug-resistance related protein 1 contributes to multidrug-resistance of mucoepidermoid carcinoma mainly via regulating multidrug-resistance protein 1: a human mucoepidermoid carcinoma cells model and Spearman's rank correlation analysis.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 27;8(8):e69611. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069611. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24013781 Free PMC article.
-
The ABC transporters MDR1 and MRP2: multiple functions in disposition of xenobiotics and drug resistance.Drug Metab Rev. 2004 Oct;36(3-4):669-701. doi: 10.1081/dmr-200033473. Drug Metab Rev. 2004. PMID: 15554242 Review.
-
Genetic polymorphisms of ATP-binding cassette transporters ABCB1 and ABCC2 and their impact on drug disposition.Curr Drug Targets. 2011 May;12(5):631-46. doi: 10.2174/138945011795378487. Curr Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21039333 Review.
Cited by
-
Overcoming ABCB1 mediated multidrug resistance in castration resistant prostate cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Aug 1;15(8):558. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06949-3. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39090086 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic polymorphisms and multiple myeloma risk: a meta-analysis.Ann Hematol. 2020 May;99(5):1017-1024. doi: 10.1007/s00277-020-03979-7. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Ann Hematol. 2020. PMID: 32162036
-
Molecular and Clinical Links between Drug-Induced Cholestasis and Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 18;24(6):5823. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065823. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On a biophysical and mathematical model of Pgp-mediated multidrug resistance: understanding the "space-time" dimension of MDR.Eur Biophys J. 2010 Jan;39(2):201-11. doi: 10.1007/s00249-009-0555-5. Epub 2009 Nov 4. Eur Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 19888571 Review.
-
Regulation of multidrug resistance 1 expression by CDX2 in ovarian mucinous adenocarcinoma.Cancer Med. 2016 Jul;5(7):1546-55. doi: 10.1002/cam4.697. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Cancer Med. 2016. PMID: 27060927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Juliano RL, Ling V. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1976; 455: 152–62. - PubMed
-
- Gottesman MM, Pastan I. Biochemistry of multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug transporter. Annu Rev Biochem 1993; 62: 385–427. - PubMed
-
- Ambudkar SV, Dey S, Hrycyna CA, Ramachandra M, Pastan I, Gottesman MM. Biochemical, cellular, and pharmacological aspects of the multidrug transporter. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 1999; 39: 361–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

