Combined modalities of resistance in an oxaliplatin-resistant human gastric cancer cell line with enhanced sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil
- PMID: 17609664
- PMCID: PMC2360324
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603866
Combined modalities of resistance in an oxaliplatin-resistant human gastric cancer cell line with enhanced sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil
Abstract
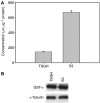
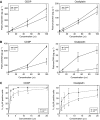
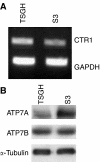
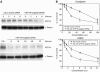
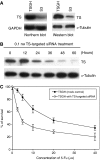
To identify mechanisms underlying oxaliplatin resistance, a subline of the human gastric adenocarcinoma TSGH cell line, S3, was made resistant to oxaliplatin by continuous selection against increasing drug concentrations. Compared with the parental TSGH cells, the S3 subline showed 58-fold resistance to oxaliplatin; it also displayed 11-, 2-, and 4.7-fold resistance to cis-diammine-dichloroplatinum (II) (CDDP), copper sulphate, and arsenic trioxide, respectively. Interestingly, S3 cells were fourfold more susceptible to 5-fluorouracil-induced cytotoxicity due to downregulation of thymidylate synthase. Despite elevated glutathione levels in S3 cells, there was no alteration of resistant phenotype to oxaliplatin or CDDP when cells were co-treated with glutathione-depleting agent, l-buthionine-(S,R)-sulphoximine. Cellular CDDP and oxaliplatin accumulation was decreased in S3 cells. In addition, amounts of oxaliplatin- and CDDP-DNA adducts in S3 cells were about 15 and 40% of those seen with TSGH cells, respectively. Western blot analysis showed increased the expression level of copper transporter ATP7A in S3 cells compared with TSGH cells. Partial reversal of the resistance of S3 cells to oxaliplatin and CDDP was observed by treating cell with ATP7A-targeted siRNA oligonucleotides or P-type ATPase-inhibitor sodium orthovanadate. Besides, host reactivation assay revealed enhanced repair of oxaliplatin- or CDDP-damaged DNA in S3 cells compared with TSGH cells. Together, our results show that the mechanism responsible for oxaliplatin and CDDP resistance in S3 cells is the combination of increased DNA repair and overexpression of ATP7A. Downregulation of thymidylate synthase in S3 cells renders them more susceptible to 5-fluorouracil-induced cytotoxicity. These findings could pave ways for future efforts to overcome oxaliplatin resistance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gene expression profiling for analysis acquired oxaliplatin resistant factors in human gastric carcinoma TSGH-S3 cells: the role of IL-6 signaling and Nrf2/AKR1C axis identification.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 Oct 1;86(7):872-87. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.07.025. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23933386
-
Oxaliplatin in treatment of the cisplatin-resistant MKN45 cell line of gastric cancer.Anticancer Res. 2008 Jul-Aug;28(4B):2087-92. Anticancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18751380
-
Improvement of sensitivity to platinum compound with siRNA knockdown of upregulated genes in platinum complex-resistant ovarian cancer cells in vitro.Biomed Pharmacother. 2009 Sep;63(8):553-60. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2008.04.006. Epub 2008 May 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2009. PMID: 18571892
-
Oxaliplatin: mechanism of action and antineoplastic activity.Semin Oncol. 1998 Apr;25(2 Suppl 5):4-12. Semin Oncol. 1998. PMID: 9609103 Review.
-
Cellular and molecular pharmacology of oxaliplatin.Mol Cancer Ther. 2002 Jan;1(3):227-35. Mol Cancer Ther. 2002. PMID: 12467217 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Bases of Mechanisms Accounting for Drug Resistance in Gastric Adenocarcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jul 30;12(8):2116. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082116. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32751679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of the proapoptotic regulator Bcl-2/adenovirus EIB 19-kDa-interacting protein 3 on the chemosensitivity of human colon cancer cell lines.Oncol Lett. 2012 Dec;4(6):1195-1202. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.933. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Oncol Lett. 2012. PMID: 23205118 Free PMC article.
-
Transport-Mediated Oxaliplatin Resistance Associated with Endogenous Overexpression of MRP2 in Caco-2 and PANC-1 Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Sep 8;11(9):1330. doi: 10.3390/cancers11091330. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31500349 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an extracellular matrix signature for predicting prognosis and sensitivity to therapy of patients with gastric cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 3;15(1):7464. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88376-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40032943 Free PMC article.
-
Txr1: an important factor in oxaliplatin resistance in gastric cancer.Med Oncol. 2014 Feb;31(2):807. doi: 10.1007/s12032-013-0807-1. Epub 2013 Dec 21. Med Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24362794
References
-
- Andrews PA, Murphy MP, Howell SB (1985) Differential potentiation of alkylating and platinating agent cytotoxicity in human ovarian carcinoma cells by glutathione depletion. Cancer Res 45: 6250–6253 - PubMed
-
- Banath JP, Olive PL (2003) Expression of phosphorylated histone H2AX as a surrogate of cell killing by drugs that create DNA double-strand breaks. Cancer Res 63: 4347–4350 - PubMed
-
- Cavanna L, Artioli F, Codignola C, Lazzaro A, Rizzi A, Gamboni A, Rota L, Rodino C, Boni F, Iop A, Zaniboni A (2006) Oxaliplatin in combination with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and leucovorin (LV) in patients with metastatic gastric cancer (MGC). Am J Clin Oncol 29: 371–375 - PubMed
-
- Cullen KJ, Newkirk KA, Schumaker LM, Aldosari N, Rone JD, Haddad BR (2003) Glutathione S-transferase pi amplification is associated with cisplatin resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines and primary tumors. Cancer Res 63: 8097–8102 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

