Dysregulation of the expression and secretion of inflammation-related adipokines by hypoxia in human adipocytes
- PMID: 17609976
- PMCID: PMC2040175
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-007-0301-8
Dysregulation of the expression and secretion of inflammation-related adipokines by hypoxia in human adipocytes
Abstract
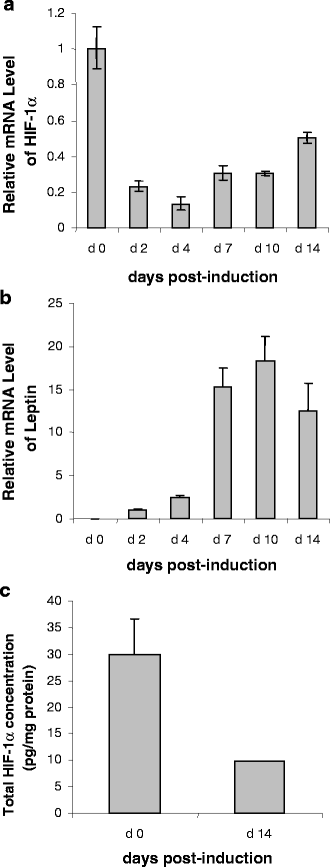
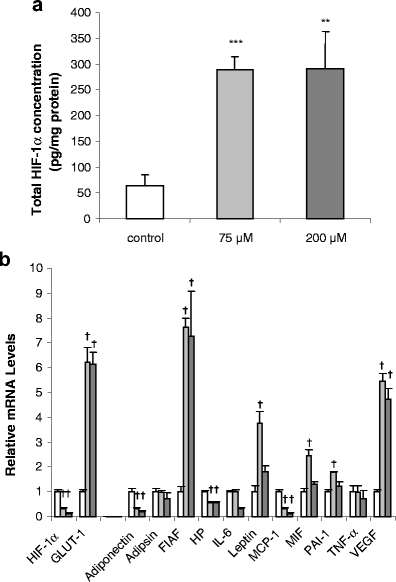
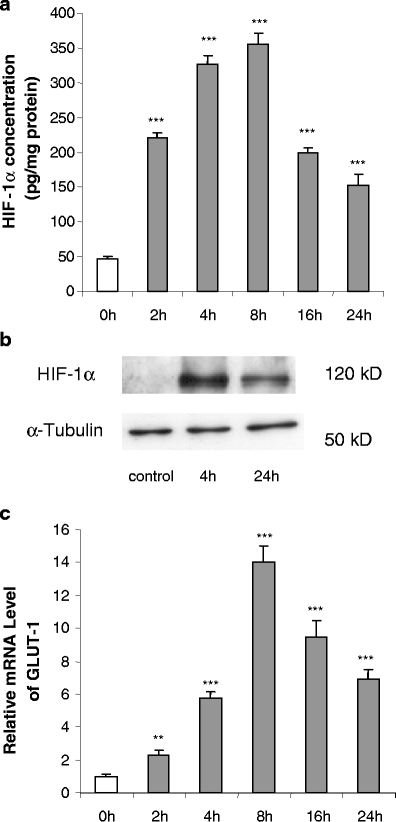
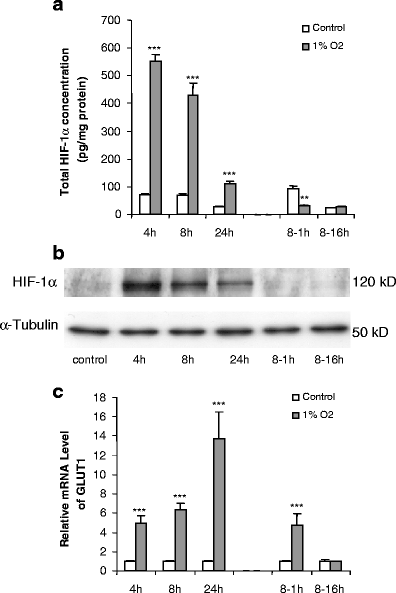
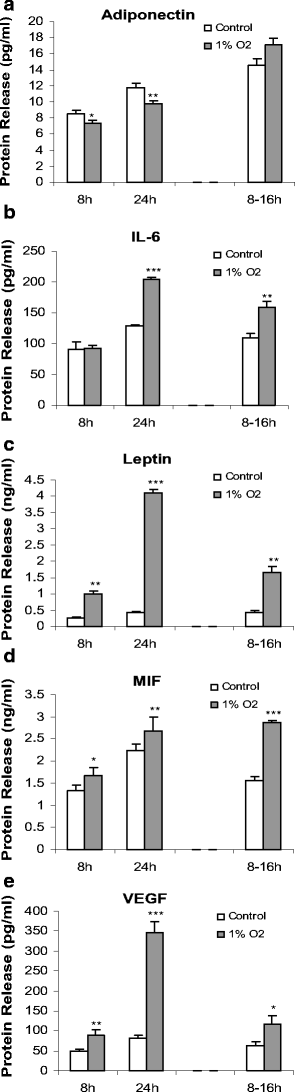
The effect of hypoxia, induced by incubation under low (1%) oxygen tension or by exposure to CoCl(2), on the expression and secretion of inflammation-related adipokines was examined in human adipocytes. Hypoxia led to a rapid and substantial increase (greater than sevenfold by 4 h of exposure to 1% O(2)) in the hypoxia-sensitive transcription factor, HIF-1alpha, in human adipocytes. This was accompanied by a major increase (up to 14-fold) in GLUT1 transporter mRNA level. Hypoxia (1% O(2) or CoCl(2)) led to a reduction (up to threefold over 24 h) in adiponectin and haptoglobin mRNA levels; adiponectin secretion also decreased. No changes were observed in TNFalpha expression. In contrast, hypoxia resulted in substantial increases in FIAF/angiopoietin-like protein 4, IL-6, leptin, MIF, PAI-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) mRNA levels. The largest increases were with FIAF (maximum 210-fold), leptin (maximum 29-fold) and VEGF (maximum 23-fold); these were reversed on return to normoxia. The secretion of IL-6, leptin, MIF and VEGF from the adipocytes was also stimulated by exposure to 1% O(2). These results demonstrate that hypoxia induces extensive changes in human adipocytes in the expression and release of inflammation-related adipokines. Hypoxia may underlie the development of the inflammatory response in adipocytes, leading to obesity-associated diseases.
Figures

References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1074/jbc.272.9.5555', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.9.5555'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9038162', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9038162/'}]}
- Behrooz A, Ismail-Beigi F (1997) Dual control of GLUT1 glucose transporter gene expression by hypoxia and by inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 272:5555–5562 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1006/jmcc.2002.2021', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1006/jmcc.2002.2021'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12099716', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12099716/'}]}
- Belanger AJ, Lu H, Date T, Liu LX, Vincent KA, Akita GY, Cheng SH, Gregory RJ, Jiang C (2002) Hypoxia up-regulates expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma angiopoietin-related gene (PGAR) in cardiomyocytes: role of hypoxia inducible factor 1α. J Mol Cell Cardiol 34:765–774 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.2337/diabetes.54.8.2277', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.54.8.2277'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16046292', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16046292/'}]}
- Cancello R, Henegar C, Viguerie N, Taleb S, Poitou C, Rouault C, Coupaye M, Pelloux V, Hugol D, Bouillot J-L, Bouloumie A, Barbatelli G, Cinti S, Svensson P-A, Barsh GS, Zucker J-D, Basdevant A, Langin D, Clément K (2005) Reduction of macrophage infiltration and chemoattractant gene expression changes in white adipose tissue of morbidly obese subjects after surgery-induced weight loss. Diabetes 54:2277–2286 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.01.004', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.01.004'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16427606', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16427606/'}]}
- Chen B, Lam KSL, Wang Y, Wu D, Lam MC, Shen J, Wong L, Hoo RLC, Zhang J, Xu A (2006) Hypoxia dysregulates the production of adiponectin and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 independent of reactive oxygen species in adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 341:549–556 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1074/jbc.M010144200', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m010144200'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11120745', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11120745/'}]}
- Chen C, Pore N, Behrooz A, Ismail-Beigi F, Maity A (2001) Regulation of GLUT1 mRNA by hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Interaction between H-ras and hypoxia. J Biol Chem 276:9519–9525 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

