MDR1-P-Glycoprotein (ABCB1) Mediates Transport of Alzheimer's amyloid-beta peptides--implications for the mechanisms of Abeta clearance at the blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 17610523
- PMCID: PMC8095502
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00075.x
MDR1-P-Glycoprotein (ABCB1) Mediates Transport of Alzheimer's amyloid-beta peptides--implications for the mechanisms of Abeta clearance at the blood-brain barrier
Abstract
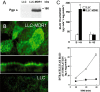
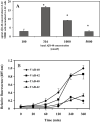
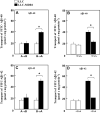
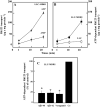
Amyloid-beta (Abeta) is the major component of the insoluble amyloid plaques that accumulate intracerebrally in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD). It has been suggested that MDR1-P-glycoprotein (ABCB1, P-gp) plays a substantial role in the elimination of Abeta from the brain. In the present study, MDR1-transfected LLC cells growing in a polarized cell layer were used to characterize the interaction of Abeta1-40/1-42 with P-gp. In this system, P-gp-mediated transport can be followed by the efflux of the fluorescent dye rhodamine-123, or of Abeta itself from the cells into the apical extracellular space. Abeta significantly decreased the apical efflux of rhodamine-123, and the transcellular transport of Abeta1-40 and Abeta1-42 into the apical chamber could be demonstrated using both ELISA and fluorescence (FITC)-labeled peptides. This transport was inhibited by a P-gp modulator. Furthermore, ATP-dependent, P-gp-mediated transport of the fluorescence-labeled peptides could be demonstrated in isolated, inside-out membrane vesicles. Our data support the concept that P-gp is important for the clearance of Abeta from brain, and thus may represent a target protein for the prevention and/or treatment of neurodegenerative disorders such as AD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The concerted amyloid-beta clearance of LRP1 and ABCB1/P-gp across the blood-brain barrier is linked by PICALM.Brain Behav Immun. 2018 Oct;73:21-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.07.017. Epub 2018 Jul 21. Brain Behav Immun. 2018. PMID: 30041013 Free PMC article.
-
New Evidence for P-gp-Mediated Export of Amyloid-β PEPTIDES in Molecular, Blood-Brain Barrier and Neuronal Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 29;22(1):246. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010246. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33383667 Free PMC article.
-
Aβ1-42 reduces P-glycoprotein in the blood-brain barrier through RAGE-NF-κB signaling.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Jun 26;5(6):e1299. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.258. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24967961 Free PMC article.
-
P-glycoprotein: a role in the export of amyloid-β in Alzheimer's disease?FEBS J. 2020 Feb;287(4):612-625. doi: 10.1111/febs.15148. Epub 2019 Dec 9. FEBS J. 2020. PMID: 31750987 Review.
-
The role of the ATP-binding cassette transporter P-glycoprotein in the transport of β-amyloid across the blood-brain barrier.Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(26):2778-86. doi: 10.2174/138161211797440168. Curr Pharm Des. 2011. PMID: 21827406 Review.
Cited by
-
Disruption in the Blood-Brain Barrier: The Missing Link between Brain and Body Inflammation in Bipolar Disorder?Neural Plast. 2015;2015:708306. doi: 10.1155/2015/708306. Epub 2015 May 13. Neural Plast. 2015. PMID: 26075104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging of cerebrovascular pathology in animal models of Alzheimer's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2014 Mar 13;6:32. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2014.00032. eCollection 2014. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24659966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increasing Intracellular Levels of Iron with Ferric Ammonium Citrate Leads to Reduced P-glycoprotein Expression in Human Immortalised Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells.Pharm Res. 2021 Jan;38(1):97-111. doi: 10.1007/s11095-021-03006-y. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 33532991
-
The Interplay of ABC Transporters in Aβ Translocation and Cholesterol Metabolism: Implicating Their Roles in Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Apr;58(4):1564-1582. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-02211-x. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 33215389 Review.
-
The blood-brain barrier in neurodegenerative disease: a rhetorical perspective.J Neurochem. 2009 Oct;111(2):291-314. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06319.x. Epub 2009 Jul 31. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 19659460 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ambudkar SV, Kim IW, Sauna ZE (2005) The power of the pump: mechanisms of action of P‐glycoprotein (ABCB1). Eur J Pharm Sci 580:1049–1055. - PubMed
-
- Bendayan R, Lee G, Bendayan M (2002) Functional expression and localization of P‐glycoprotein at the blood brain barrier. Microsc Res Tech 57:365–380. - PubMed
-
- Cirrito JR, Deane R, Fagan AM, Spinner ML, Parsadanian M, Finn MB, Jiang H, Prior JL, Sagare A, Bales KR, Paul SM, Zlokovic BV, Piwnica‐Worms D, Holtzman DM (2005) P‐glycoprotein deficiency at the blood‐brain barrier increases amyloid‐beta deposition in an Alzheimer disease mouse model. J Clin Invest 115:3285–3290. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cummings J (2004) Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 351:56–67. - PubMed
-
- Deane R, Wu Z, Zlokovic BV (2004) RAGE (yin) versus LRP (yang) balance regulates Alzheimer amyloid beta‐peptide clearance through transport across the blood‐brain barrier. Stroke 35(11 Suppl. 1):2628–2631. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

