Alpha-beta T cells provide protection against lethal encephalitis in the murine model of VEEV infection
- PMID: 17610927
- PMCID: PMC2067255
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.05.041
Alpha-beta T cells provide protection against lethal encephalitis in the murine model of VEEV infection
Abstract
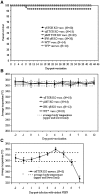
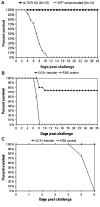
We evaluated the safety and immunogenicity of a chimeric alphavirus vaccine candidate in mice with selective immunodeficiencies. This vaccine candidate was highly attenuated in mice with deficiencies in the B and T cell compartments, as well as in mice with deficient gamma-interferon responsiveness. However, the level of protection varied among the strains tested. Wild type mice were protected against lethal VEEV challenge. In contrast, alpha/beta (alphabeta) TCR-deficient mice developed lethal encephalitis following VEEV challenge, while mice deficient in gamma/delta (gammadelta) T cells were protected. Surprisingly, the vaccine potency was diminished by 50% in animals lacking interferon-gamma receptor alpha chain (R1)-chain and a minority of vaccinated immunoglobulin heavy chain-deficient (microMT) mice survived challenge, which suggests that neutralizing antibody may not be absolutely required for protection. Prolonged replication of encephalitic VEEV in the brain of pre-immunized mice is not lethal and adoptive transfer experiments indicate that CD3(+) T cells are required for protection.
Figures




References
-
- Agrati C., Castilletti C., De Santis R., Cimini E., Bordi L., Malkovsky M., Poccia F., Capobianchi M.R. Interferon- gamma -mediated antiviral immunity against orthopoxvirus infection is provided by gamma delta T cells. J. Infect. Dis. 2006;193(11):1606–1607. - PubMed
-
- Altman D.G. Practical Statistics for Medical Research. Chapman and Hall; London: 1991. Analysis of survival times.
-
- Beaty B.J., Calisher C.H., Shope R.E. Arboviruses. In: Schmidt N.J., Emmons R.W., editors. Diagnostic Procedures for Viral, Rickettsial and Chlamydial Infections. 6th edition. American Public Health Association; Washington, DC: 1989. pp. 797–855.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

