Mapping human whole-brain structural networks with diffusion MRI
- PMID: 17611629
- PMCID: PMC1895920
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000597
Mapping human whole-brain structural networks with diffusion MRI
Abstract
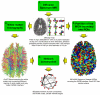
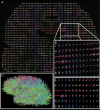
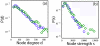
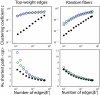
Understanding the large-scale structural network formed by neurons is a major challenge in system neuroscience. A detailed connectivity map covering the entire brain would therefore be of great value. Based on diffusion MRI, we propose an efficient methodology to generate large, comprehensive and individual white matter connectional datasets of the living or dead, human or animal brain. This non-invasive tool enables us to study the basic and potentially complex network properties of the entire brain. For two human subjects we find that their individual brain networks have an exponential node degree distribution and that their global organization is in the form of a small world.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

