The influence of postoperative coronal alignment on revision surgery in total knee arthroplasty
- PMID: 17611758
- PMCID: PMC2551715
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-007-0391-0
The influence of postoperative coronal alignment on revision surgery in total knee arthroplasty
Abstract
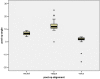
This study examines the association between postoperative coronal tibiofemoral alignment and revision surgery in knee arthroplasty. We retrospectively reviewed the case notes and post-operative long-leg radiographs of 197 Kinemax knee arthroplasty with mean follow-up of 9 years (SD 2.2). They were divided into three groups: neutral, valgus and varus. Revision or decision to revise was used as a hard endpoint. There was no statistical difference among the three groups (p=0.78). We conclude that aseptic failure of a total knee is multifactorial. Coronal tibio-femoral alignment may not be as important a cause of failure as has been previously thought.
Cette étude a pour but d’examiner l’alignement des éléments prothétiques dans la chirurgie de reprise de prothèse totale du genou. Nous avons de façon rétrospective revu en 1997 une série de prothèses de type Kinemax avec un suivi moyen de 9 ans (SD 2.2). La population a été divisée en trois groupes : Neutre, Valgus et Varus. Pour les courbes de survie ont été utilisées comme référence la révision ou la décision de révision. Nous pouvons conclure que le descellement aseptique d’une prothèse totale du genou est multi factorielle. L’alignement tibio fémoral n’est pas une cause importante d’échec comme l’on pouvait le penser auparavant.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Current opinions about coronal plane alignment in total knee arthroplasty: A survey article.Acta Orthop Belg. 2015 Sep;81(3):471-7. Acta Orthop Belg. 2015. PMID: 26435243
-
Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: just how important is it?J Arthroplasty. 2009 Sep;24(6 Suppl):39-43. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2009.04.034. Epub 2009 Jun 24. J Arthroplasty. 2009. PMID: 19553073
-
Convincing long-term results independent from the postoperative leg alignment following cementless total knee arthroplasty.Knee. 2020 Mar;27(2):552-557. doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2019.11.016. Epub 2019 Dec 26. Knee. 2020. PMID: 31883762
-
Shorter survival rate in varus-aligned knees after total knee arthroplasty.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016 Aug;24(8):2663-71. doi: 10.1007/s00167-015-3781-7. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016. PMID: 26377095 Review.
-
A case for one-stage revision in infected total knee arthroplasty?Knee. 2011 Jan;18(1):1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2010.04.008. Epub 2010 Aug 17. Knee. 2011. PMID: 20719522 Review.
Cited by
-
Minimal under-correction gives better outcomes following total knee arthroplasty in severe varus knees-myth or reality?-analysis of one hundred sixty two knees with varus greater than fifteen degrees.Int Orthop. 2020 Apr;44(4):715-723. doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-4240-0. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Int Orthop. 2020. PMID: 30460462
-
Static Baropodometry for Assessing Short-Term Functional Outcome after Unilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty: Exploring Correlation between Static Plantar Pressure Measurements and Self-Reported Outcomes.J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 3;12(21):6917. doi: 10.3390/jcm12216917. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37959381 Free PMC article.
-
Slight undercorrection following total knee arthroplasty results in superior clinical outcomes in varus knees.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013 Oct;21(10):2325-30. doi: 10.1007/s00167-013-2481-4. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013. PMID: 23552665 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation and validation of 2D biomechanical models of the knee for radiograph-based preoperative planning in total knee arthroplasty.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 8;15(1):e0227272. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227272. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31914159 Free PMC article.
-
Restricted kinematic alignment in primary total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review of radiographic and clinical data.J Orthop. 2022 Jul 2;33:37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2022.06.014. eCollection 2022 Sep-Oct. J Orthop. 2022. PMID: 35812351 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bargren JH, Blaha JD, Freeman MAR. Alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983;173:178–183. - PubMed
-
- Freeman MAR, Todd RC, Bambert P, et al. ICLH arthroplsty of the knee: 1968–1977. J Bone Joint Surg. 1978;60-B:339–344. - PubMed
-
- Hood RW, Vanni M, Insall JN. The correction of knee alignment in 225 consecutive total condylar knee replacement. Clin Orthop. 1981;160:94–105. - PubMed
-
- Insall JN, Binazzi R, Soudry M, et al. Total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;192:13–22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical