Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) inhibits glutamatergic synaptic transmission in dorsolateral periaqueductal gray (dl-PAG)
- PMID: 17612511
- PMCID: PMC2030489
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.06.004
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) inhibits glutamatergic synaptic transmission in dorsolateral periaqueductal gray (dl-PAG)
Abstract
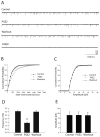
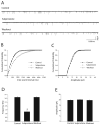
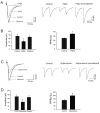
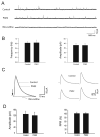
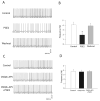
The purpose of this study was to determine the role of prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) in modulating neuronal activity of the dorsolateral periaqueductal gray (dl-PAG) through excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs. First, whole cell voltage-clamp recording was performed to obtain excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs and IPSCs) of the dl-PAG neurons. Our results show that PGE(2) significantly decreased the frequency of miniature EPSCs and amplitude of evoked EPSCs. The effects were mimicked by sulprostone, an agonist to PGE(2) EP(3) receptors. In contrast, PGE(2) had no distinct effect on IPSCs. In addition, spontaneous action potential of the dl-PAG neurons was recorded using whole cell current-clamp methods. PGE(2) significantly attenuated the discharge rate of the dl-PAG neurons. The decreased firing activity was abolished in the presence of glutamate NMDA and non-NMDA receptor antagonists. The results from the current study provide the first evidence indicating that PGE(2) inhibits the neuronal activity of the dl-PAG via selective attenuation of glutamatergic synaptic inputs, likely due to the activation of presynaptic EP(3) receptors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Purinergic P2X receptors presynaptically increase glutamatergic synaptic transmission in dorsolateral periaqueductal gray.Brain Res. 2008 May 7;1208:46-55. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.02.083. Epub 2008 Mar 8. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18395189 Free PMC article.
-
TRPV1 receptor mediates glutamatergic synaptic input to dorsolateral periaqueductal gray (dl-PAG) neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2007 Jan;97(1):503-11. doi: 10.1152/jn.01023.2006. Epub 2006 Oct 25. J Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17065246
-
Role of GABA receptors in nitric oxide inhibition of dorsolateral periaqueductal gray neurons.Neuropharmacology. 2008 Mar;54(4):734-44. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.12.008. Epub 2008 Jan 28. Neuropharmacology. 2008. PMID: 18222497 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2 depresses solitary tract-mediated synaptic transmission in the nucleus tractus solitarius.Neuroscience. 2007 May 11;146(2):792-801. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.01.053. Epub 2007 Mar 23. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17367942 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic inhibitory action of opioids on synaptic transmission in the rat periaqueductal grey in vitro.J Physiol. 1997 Jan 15;498 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):463-72. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1997.sp021872. J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9032693 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The important role of CNS facilitation and inhibition for chronic pain.Int J Clin Rheumtol. 2013 Dec 1;8(6):639-646. doi: 10.2217/ijr.13.57. Int J Clin Rheumtol. 2013. PMID: 24489609 Free PMC article.
-
EP1 receptor within the ventrolateral periaqueductal grey controls thermonociception and rostral ventromedial medulla cell activity in healthy and neuropathic rat.Mol Pain. 2011 Oct 24;7:82. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-7-82. Mol Pain. 2011. PMID: 22023852 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II inhibits GABAergic synaptic transmission in dorsolateral periaqueductal gray neurons.Neurosci Lett. 2009 May 8;455(1):8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.03.063. Epub 2009 Mar 24. Neurosci Lett. 2009. PMID: 19429096 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of rat locus coeruleus neurons by prostaglandin E2 EP3 receptors: pharmacological characterization ex vivo.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 15;14:1290605. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1290605. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38035000 Free PMC article.
-
Periaqueductal grey cyclooxygenase-dependent facilitation of C-nociceptive drive and encoding in dorsal horn neurons in the rat.J Physiol. 2014 Nov 15;592(22):5093-107. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.275909. Epub 2014 Sep 19. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25239460 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albin RL, Makowiec RL, Hollingsworth Z, Dure LS, Penney JB, Young AB. Excitatory amino acid receptors in the periaqueductal gray of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1990;118:112–115. - PubMed
-
- Bandler R, Carrive P, Zhang SH. Integration of somatic and autonomic reactions within the midbrain periaqueductal gray: Viscerotopic, somatotopic and functional organization. Prog In Brain Res. 1991;87:269–305. - PubMed
-
- Barbaresi P. GABA-immunoreactive neurons and terminals in the cat periaqueductal gray matter: a light and electron microscopic study. Journal of Neurocytology. 2005;34:471–87. - PubMed
-
- Behbehani MM. Functional characteristics of the midbrain periaqueductal gray. Prog Neurobiol. 1995;46:575–605. - PubMed
-
- Beitz AJ, Williams FG. Localization of putative amino acid transmitters in the PAG and their relationship to the PAG–raphe magnus pathway. In: Depaulis A, Bandler R, editors. The Midbrain Periaqueductal Gray Matter. Plenum; New York: 1991.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

