Lipoteichoic acid may affect the pathogenesis of PBC-like bile duct damage and might be involved in systemic multifocal epithelial inflammations in chronic colitis-harboring TCRalpha-/-xAIM-/- mice
- PMID: 17612899
- PMCID: PMC2409170
- DOI: 10.1080/08916930701402392
Lipoteichoic acid may affect the pathogenesis of PBC-like bile duct damage and might be involved in systemic multifocal epithelial inflammations in chronic colitis-harboring TCRalpha-/-xAIM-/- mice
Abstract
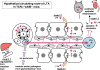
Background: Chronic colitis-harboring TCRalpha(- / - ) x AIM(- / - ) mice showed PBC-like bile duct damage in the liver. Bacterial infection is one of the candidates for the pathogenesis of PBC. We demonstrated that the bacterial cell wall component lipotheicoic acid (LTA) was detected at sites of inflammation around damaged bile ducts in PBC patients. The aim of this study was to investigate the pathophysiology of the liver and other organs in TCRalpha(- / - ) x AIM(- / - ) mice.
Methods: Thirteen female TCRalpha(- / - ) x AIM(- / - ) mice were sacrificed at 24 weeks of age. The liver, stomach, small intestine, colon, pancreas, kidney and spleen were studied for pathological examination. Using anti-LTA antibody as the primary antibody, an immunohistochemical study was carried out.
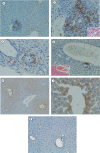
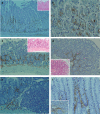
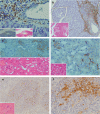
Results: In the liver, LTA was mainly detected in the portal area with inflammation, and some of the cytoplasm of hepatocytes. Inflammations were also observed in the stomach, intestine, pancreas and kidney. Throughout the gastrointestinal tract, from the stomach to the colon, LTA was detected in the epithelium at sites of inflammation. Furthermore, LTA was detected around both pancreatic ducts with inflammation and distal renal tubules with inflammation.
Conclusions: The development of inflammations in the liver as well as extensive organs, strongly suggests a close relationship between bile duct damage and systemic multifocal epithelial inflammations, perhaps involving bacterial LTA, in TCRalpha(- / - ) x AIM(- / - ) mice.
Figures
References
-
- Haruta I, Hashimoto E, Kato Y, Miyakawa H, Shibata N, Kobayashi M, et al. Intrahepatic biliary epithelial cell damage and inflammation in portal tract associated with chronic colitis-harboring TCRα−/− mice. Hepatol Res. 2006;34:3–8. - PubMed
-
- Haruta I, Kato Y, Hashimoto E, Minjares C, Kennedy S, Uto H, et al. Assocation of AIM, anovel apoptosis inhibitory factor, with hepatitis via supporting macrophage survival and enhancing phagocytotic function of macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:22910–22914. - PubMed
-
- Arai S, Shelton JM, Chen M, Bradley MN, Castrillo A, Bookout AL, et al. Arole for the apoptosis inhibitory factor AIM/Sp alpha/Api6 in atherosclerosis development. Cell Metabol. 2005;1:201–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
