Group VIA phospholipase A2 (iPLA2beta) participates in angiotensin II-induced transcriptional up-regulation of regulator of g-protein signaling-2 in vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 17613534
- PMCID: PMC2096773
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M611206200
Group VIA phospholipase A2 (iPLA2beta) participates in angiotensin II-induced transcriptional up-regulation of regulator of g-protein signaling-2 in vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
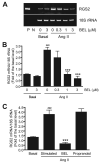
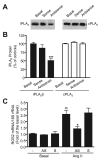
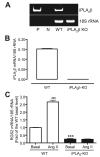
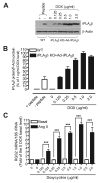
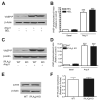
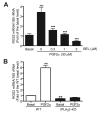
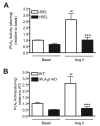
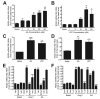
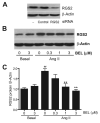
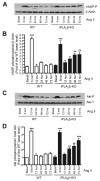
Rgs2 (regulator of G-protein signaling-2)-deficient mice exhibit severe hypertension, and genetic variations of RGS2 occur in hypertensive patients. RGS2 mRNA up-regulation by angiotensin II (Ang II) in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) is a potentially important negative feedback mechanism in blood pressure homeostasis, but how it occurs is unknown. Here we demonstrate that group VIA phospholipase A2 (iPLA2beta) plays a pivotal role in Ang II-induced RGS2 mRNA up-regulation in VSMC by three independent approaches, including pharmacologic inhibition with a bromoenol lactone suicide substrate, suppression of iPLA2beta expression with antisense oligonucleotides, and genetic deletion in iPLA2beta-null mice. Selective inhibition of iPLA2beta by each of these approaches abolishes Ang II-induced RGS2 mRNA up-regulation. Furthermore, using adenovirus-mediated gene transfer, we demonstrate that restoration of iPLA2beta-expression in iPLA2beta-null VSMC reconstitutes the ability of Ang II to up-regulate RGS2 mRNA expression. In contrast, Ang II-induced vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein phosphorylation and Ang II receptor expression are unaffected. Moreover, in wild-type but not iPLA2beta-null VSMC, Ang II stimulates iPLA2 enzymatic activity significantly. Both arachidonic acid and lysophosphatidylcholine, products of iPLA2beta action, induce RGS2 mRNA up-regulation. Inhibition of lipoxygenases, particularly 15-lipoxygenase, and cyclooxygenases, but not cytochrome P450-dependent epoxygenases inhibits Ang II- or AA-induced RGS2 mRNA expression. Moreover, RGS2 protein expression is also up-regulated by Ang II, and this is attenuated by bromoenol lactone. Disruption of the Ang II/iPLA2beta/RGS2 feedback pathway in iPLA2beta-null cells potentiates Ang II-induced vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein and Akt phosphorylation in a time-dependent manner. Collectively, our results demonstrate that iPLA2beta participates in Ang II-induced transcriptional up-regulation of RGS2 in VSMC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of a cAMP-response element in the regulator of G-protein signaling-2 (RGS2) promoter as a key cis-regulatory element for RGS2 transcriptional regulation by angiotensin II in cultured vascular smooth muscles.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 30;286(52):44646-58. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.265462. Epub 2011 Nov 4. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 22057271 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II-induced Akt activation is mediated by metabolites of arachidonic acid generated by CaMKII-stimulated Ca2(+)-dependent phospholipase A2.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005 May;288(5):H2306-16. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00571.2004. Epub 2005 Jan 6. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15637121
-
The angiotensin II receptor antagonist, losartan, enhances regulator of G protein signaling 2 mRNA expression in vascular smooth muscle cells of Wistar rats.Hypertens Res. 2016 May;39(5):295-301. doi: 10.1038/hr.2015.154. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Hypertens Res. 2016. PMID: 26763849
-
The expression and function of a group VIA calcium-independent phospholipase A2 (iPLA2beta) in beta-cells.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2004 Oct;82(10):824-32. doi: 10.1139/y04-064. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15573142 Review.
-
Deregulation of RGS2 in cardiovascular diseases.Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2010 Jan 1;2(2):547-57. doi: 10.2741/s84. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2010. PMID: 20036967 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of calcium-independent phospholipase A2beta in high glucose-induced activation of RhoA, Rho kinase, and CPI-17 in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells and vascular smooth muscle hypercontractility in diabetic animals.J Biol Chem. 2010 Mar 19;285(12):8628-38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.057711. Epub 2010 Jan 19. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20086008 Free PMC article.
-
Role of sympathetic pathway in light-phase time-restricted feeding-induced blood pressure circadian rhythm alteration.Front Nutr. 2022 Sep 8;9:969345. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.969345. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36159491 Free PMC article.
-
Smooth-muscle BMAL1 participates in blood pressure circadian rhythm regulation.J Clin Invest. 2015 Jan;125(1):324-36. doi: 10.1172/JCI76881. Epub 2014 Dec 8. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 25485682 Free PMC article.
-
Group VIA PLA2 (iPLA2β) is activated upstream of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in pancreatic islet β-cell signaling.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 17;287(8):5528-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.285114. Epub 2011 Dec 22. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22194610 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic ablation of calcium-independent phospholipase A(2)beta causes hypercontractility and markedly attenuates endothelium-dependent relaxation to acetylcholine.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Jun;298(6):H2208-20. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00839.2009. Epub 2010 Apr 9. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20382858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wieland T, Chen CK. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 1999;360:14–26. - PubMed
-
- Heximer SP, Srinivasa SP, Bernstein LS, Bernard JL, Linder ME, Hepler JR, Blumer KJ. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:34253–34259. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Hashim S, Anand-Srivastava MB. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005;66:503–511. - PubMed
-
- Sinnarajah S, Dessauer CW, Srikumar D, Chen J, Yuen J, Yilma S, Dennis JC, Morrison EE, Vodyanoy V, Kehrl JH. Nature. 2001;409:1051–1055. - PubMed
-
- Kehrl JH, Sinnarajah S. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002;34:432–438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

