Immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated cross-reactivity between mesquite pollen proteins and lima bean, an edible legume
- PMID: 17614972
- PMCID: PMC2219328
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03446.x
Immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated cross-reactivity between mesquite pollen proteins and lima bean, an edible legume
Abstract
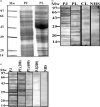
Immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated food allergy often develops as a consequence of allergic sensitization to pollen proteins. Mesquite (Prosopis juliflora) tree pollen is reported to be cross-reactive with other pollen species, but little has been reported on its cross-reactivity with plant-derived foods belonging to the same/different families. The present study investigates the in vitro cross-reactivity of mesquite pollen and lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus), an edible seed belonging to the Leguminosae family. Of 110 patients (asthma, rhinitis or both) tested intradermally, 20 showed marked positive reactions with Prosopis pollen extract. Of these, 12 patients showed elevated specific IgE to Prosopis pollen extract alone and four to both Phaseolus and pollen extract. In vitro cross-reactivity was investigated using inhibition assays [enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) inhibition, immunoblot inhibition], histamine release and lymphoproliferation. P. lunatus extract could inhibit IgE binding to P. juliflora in a dose-dependent manner, requiring 400 ng of protein for 50% inhibition in ELISA assay. Immunoblot and immunoblot inhibition demonstrated the presence of 20, 26, 35, 66 and 72 kDa as shared IgE binding components between the two extracts. Histamine release, peripheral blood mononuclear cells proliferation and interleukin (IL)-4 levels also suggested allergenic cross-reactivity. In conclusion, there is humoral and cellular cross-reactivity between Prosopis pollen and Phaseolus seed allergens.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Invasive Mesquite (Prosopis juliflora), an Allergy and Health Challenge.Plants (Basel). 2020 Jan 22;9(2):141. doi: 10.3390/plants9020141. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31979176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A clinically relevant major cross-reactive allergen from mesquite tree pollen.Eur J Clin Invest. 2008 Oct;38(10):774-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2008.02020.x. Eur J Clin Invest. 2008. PMID: 18837803
-
Analysis of IgE binding proteins of mesquite (Prosopis juliflora) pollen and cross-reactivity with predominant tree pollens.Immunobiology. 2006;211(9):733-40. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2006.03.003. Epub 2006 May 9. Immunobiology. 2006. PMID: 17015148
-
Immunochemical characterization of prosopis juliflora pollen allergens and evaluation of cross-reactivity pattern with the most allergenic pollens in tropical areas.Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015 Feb;14(1):74-82. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25530142
-
[Legume cross-reactivity].Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2003 May-Jun;31(3):151-61. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2003. PMID: 12783766 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive review of legume allergy.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2013 Aug;45(1):30-46. doi: 10.1007/s12016-012-8310-6. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2013. PMID: 22555630 Review.
-
Invasive Mesquite (Prosopis juliflora), an Allergy and Health Challenge.Plants (Basel). 2020 Jan 22;9(2):141. doi: 10.3390/plants9020141. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31979176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurotoxicity of Prosopis juliflora: from Natural Poisoning to Mechanism of Action of Its Piperidine Alkaloids.Neurotox Res. 2018 Nov;34(4):878-888. doi: 10.1007/s12640-017-9862-2. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Neurotox Res. 2018. PMID: 29340871 Review.
-
Immediate hypersensitivity to common food allergens: an investigation on food sensitization in respiratory allergic patients of calcutta, India.World Allergy Organ J. 2009 Jan;2(1):9-12. doi: 10.1097/WOX.0b013e318194c0de. World Allergy Organ J. 2009. PMID: 23282888 Free PMC article.
-
Legume Allergens Pea, Chickpea, Lentil, Lupine and Beyond.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024 Sep;24(9):527-548. doi: 10.1007/s11882-024-01165-7. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024. PMID: 38990406 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Valenta R, Kraft D. Type 1 allergic reactions to plant-derived food: a consequence of primary sensitization to pollen allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996;97:893–5. - PubMed
-
- Mittag D, Vieths S, Vogel L, et al. Birch pollen-related food allergy to legumes: identification and characterization of the Bet v 1 homologue in mungbean (Vigna radiata), Vig r1. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005;35:1049–55. - PubMed
-
- Vieths S, Scheurer S, Ballmer-Weber BK. Current understanding of cross-reactivity of food allergens and pollen. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2002;964:47–68. - PubMed
-
- Tuft L, Blumstein GI. Studies in food allergy. II. Sensitization to fresh fruits: clinical and experimental observations. J Allergy. 1942;13:574–82.
-
- Eriksson NE, Wihl JA, Arrendal H. Birch pollen-related food hypersensitivity: influence of total and specific IgE levels. A multicenter study. Allergy. 1983;38:353–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

