Accuracy of computed tomography perfusion in assessing metastatic involvement of enlarged axillary lymph nodes in patients with breast cancer
- PMID: 17615058
- PMCID: PMC2206711
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr1738
Accuracy of computed tomography perfusion in assessing metastatic involvement of enlarged axillary lymph nodes in patients with breast cancer
Abstract
Introduction: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of computed tomography (CT) perfusion in differentiating metastatic from inflammatory enlarged axillary lymph nodes in patients with breast cancer.
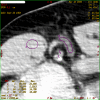
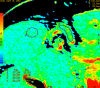
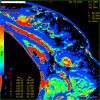
Methods: Twenty-five patients with 26 locally advanced breast tumors and clinically palpable axillary lymph nodes underwent dynamic multi-detector CT (LightSpeed 16; General Electric Company) at one scan per second for 150 seconds at the same table position after 40 ml intravenous contrast injection at 4.0 ml/second. Semi-automatic calculation of values of perfusion parameters - blood flow (BF), blood volume (BV), mean transit time (MTT), and permeability surface (PS) - was performed. Results were compared with pathology and with Her-2/neu and Ki-67 levels in a surgical specimen of the primary tumor.
Results: Examined lymph nodes were inflammatory in 8 cases and metastatic in 18. Mean values of perfusion parameters in inflammatory and metastatic nodes, respectively, were BF of 76.18 (confidence interval [CI], 31.53) and 161.60 (CI, 40.94) ml/100 mg per minute (p < 0.05), BV of 5.81 (CI, 2.50) and 9.15 (CI, 3.02) ml/100 mg (not significant [n.s.]), MTT of 6.80 (CI, 1.55) and 5.50 (CI, 1.84) seconds (p = 0.07), and PS of 25.82 (CI, 4.62) and 25.96 (CI, 7.47) ml/100 mg per minute (n.s.). Size of nodes, stage of breast cancer, Ki-67 and Her-2/neu levels in breast cancer, and expression of primary tumor activity were not correlated to any perfusion parameter in metastatic nodes.
Conclusion: CT perfusion might be an effective tool for studying enlarged axillary lymph nodes in patients with breast cancer. It gives information on vascularization of lymph nodes, helping to understand the changes occurring when neoplastic cells implant in lymph nodes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced MRI at 3 T for accurate axillary staging in breast cancer.Br J Surg. 2016 Jan;103(1):60-9. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10040. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Br J Surg. 2016. PMID: 26572241 Clinical Trial.
-
99mTc-Tetrofosmin pinhole-SPECT (P-SPECT) and radioguided sentinel node (SN) biopsy and in breast cancer axillary lymph node staging.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2001 Dec;16(6):501-13. doi: 10.1089/10849780152752100. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2001. PMID: 11789027
-
Detection of extra-axillary lymph node involvement with FDG PET/CT in patients with stage II-III breast cancer.Eur J Cancer. 2010 Dec;46(18):3205-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.07.034. Epub 2010 Aug 16. Eur J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20719497
-
Staging of women with breast cancer after introduction of sentinel node guided axillary dissection.Dan Med J. 2012 Jul;59(7):B4475. Dan Med J. 2012. PMID: 22759850 Review.
-
[Imaging techniques for axillary lymph node staging in breast cancer].Rev Med Univ Navarra. 2004 Jul-Sep;48(3):9-13. Rev Med Univ Navarra. 2004. PMID: 15622920 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of cervical lymph nodes with CT perfusion in patients with hypopharyngeal and laryngeal squamous cell cancer.Pol J Radiol. 2011 Jan;76(1):7-13. Pol J Radiol. 2011. PMID: 22802810 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative analysis for breast density estimation in low dose chest CT scans.J Med Syst. 2014 Mar;38(3):21. doi: 10.1007/s10916-014-0021-5. Epub 2014 Mar 19. J Med Syst. 2014. PMID: 24643751
-
Accuracy of perfusion MRI with high spatial but low temporal resolution to assess invasive breast cancer response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a retrospective study.BMC Cancer. 2011 Aug 19;11:361. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-361. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21854572 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic-flow relationships in primary breast cancer: feasibility of combined PET/dynamic contrast-enhanced CT.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009 Mar;36(3):416-21. doi: 10.1007/s00259-008-0948-1. Epub 2008 Sep 26. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009. PMID: 18818917
-
Assessment of the spatial pattern of colorectal tumour perfusion estimated at perfusion CT using two-dimensional fractal analysis.Eur Radiol. 2009 Jun;19(6):1358-65. doi: 10.1007/s00330-009-1304-y. Epub 2009 Feb 4. Eur Radiol. 2009. PMID: 19190914
References
-
- Fidler IJ. Molecular biology of cancer: invasion and metastasis. In: Devita VT, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA, editor. Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. 5. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott-Raven; 1997. pp. 135–152.
-
- Cotran RS, Kumar V, Tucker C. Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease. 6. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Co; 1999. Neoplasia; pp. 268–271.
-
- Sleeman JP. The lymph node as a bridgehead in the metastatic dissemination of tumors. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2000;157:55–81. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

