Multiple activation mechanisms of store-operated TRPC channels in smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 17615095
- PMCID: PMC2277241
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.137802
Multiple activation mechanisms of store-operated TRPC channels in smooth muscle cells
Abstract
Store-operated channels (SOCs) are plasma membrane Ca2+-permeable cation channels which are activated by agents that deplete intracellular Ca2+ stores. In smooth muscle SOCs are involved in contraction, gene expression, cell growth and proliferation. Single channel recording has demonstrated that SOCs with different biophysical properties are expressed in smooth muscle indicating diverse molecular identities. Moreover it is apparent that several gating mechanisms including calmodulin, protein kinase C and lysophospholipids are involved in SOC activation. Evidence is accumulating that TRPC proteins are important components of SOCs in smooth muscle. More recently Orai and STIM proteins have been proposed to underlie the well-described calcium-release-activated current (ICRAC) in non-excitable cells but at present there is little information on the role of Orai and STIM proteins in smooth muscle. In addition it is likely that different TRPC subunits coassemble as heterotetrameric structures to form smooth muscle SOCs. In this brief review we summarize the diverse properties and gating mechanisms of SOCs in smooth muscle. We propose that the heterogeneity of the properties of these conductances in smooth muscle results from the formation of heterotetrameric TRPC structures in different smooth muscle preparations.
Figures

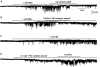

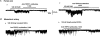
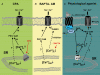
References
-
- Ahmmed GU, Mehta D, Vogel S, Holinstat M, Paria BC, Tiruppathi C, Malik AB. Protein kinase Cα phosphorylates transient receptor potential channel-1 (TRPC1) and regulates store-operated Ca2+ entry. Role in signalling increased endothelial permeability. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:20941–20949. - PubMed
-
- Albert AP, Large WA. Store-operated Ca2+-permeable non-selective cation channels in smooth muscle cells. Cell Calcium. 2003;33:345–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

