Depolarization activates the phosphoinositide phosphatase Ci-VSP, as detected in Xenopus oocytes coexpressing sensors of PIP2
- PMID: 17615106
- PMCID: PMC2277204
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.134775
Depolarization activates the phosphoinositide phosphatase Ci-VSP, as detected in Xenopus oocytes coexpressing sensors of PIP2
Abstract
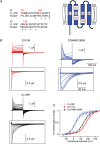
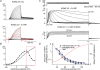
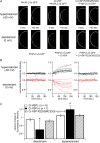
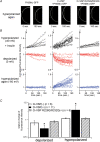
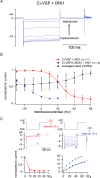
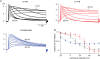
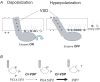
Voltage-evoked signals play critical roles in neural activities, muscle contraction and exocytosis. Ciona voltage-sensor containing phosphatase (Ci-VSP) consists of the transmembrane voltage sensor domain (VSD) and a cytoplasmic domain of phosphoinositide phosphatase, homologous to phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN). Previous experiments utilizing potassium channels as the sensor for phosphoinositides have demonstrated that phosphatase activities of Ci-VSP are voltage dependent. However, it still remained unclear whether enzyme activity is activated by depolarization or hyperpolarization. Further, a large gap in voltage dependency was found between the charge movement of the VSD and potassium channel-reporting phosphatase activities. In this study, voltage-dependent dynamics of phosphoinositides mediated by Ci-VSP were examined by confocal imaging and electrical measurements in Xenopus oocytes. Imaging of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P(2)) using green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged pleckstrin homology (PH) domains from phospholipase C delta subunit (PLC-delta) showed that PtdIns(4,5)P(2) concentration is reduced during depolarization. In the presence of Ci-VSP, IRK1 channels with higher sensitivity to phosphoinositide than GIRK2 channels decreased their magnitude during depolarization over 0 mV, indicating that the PtdIns(4,5)P(2) level is reduced upon depolarization. KCNQ2/3 channels coexpressed with Ci-VSP exhibited voltage-dependent decay of the outward current that became sharper with higher depolarization in a voltage range up to 100 mV. These results indicate that Ci-VSP has an activity that depletes PtdIns(4,5)P(2) unlike PTEN and that depolarization-activated voltage sensor movement is translated into activation of phosphatase activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Coupling of the phosphatase activity of Ci-VSP to its voltage sensor activity over the entire range of voltage sensitivity.J Physiol. 2011 Jun 1;589(Pt 11):2687-705. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.208165. Epub 2011 Apr 4. J Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21486809 Free PMC article.
-
A voltage-sensing phosphatase, Ci-VSP, which shares sequence identity with PTEN, dephosphorylates phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jun 10;105(23):7970-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803936105. Epub 2008 Jun 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18524949 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage- and Ca2+-inducible PLC activity for analyzing PI(4,5)P2 sensitivity of ion channels in Xenopus oocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2025 Jan;1867(1):184396. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2024.184396. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2025. PMID: 39481747
-
Electrifying phosphatases.Sci STKE. 2005 Oct 25;2005(307):pe50. doi: 10.1126/stke.3072005pe50. Sci STKE. 2005. PMID: 16249403 Review.
-
Voltage-sensing phosphatase: its molecular relationship with PTEN.Physiology (Bethesda). 2011 Feb;26(1):6-13. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00035.2010. Physiology (Bethesda). 2011. PMID: 21357898 Review.
Cited by
-
A human phospholipid phosphatase activated by a transmembrane control module.J Lipid Res. 2012 Nov;53(11):2266-74. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M026021. Epub 2012 Aug 15. J Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22896666 Free PMC article.
-
Role of K364 next to the active site cysteine in voltage-dependent phosphatase activity of Ci-VSP.Biophys J. 2023 Jun 6;122(11):2267-2284. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.01.022. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Biophys J. 2023. PMID: 36680342 Free PMC article.
-
Triclosan is a KCNQ3 potassium channel activator.Pflugers Arch. 2022 Jul;474(7):721-732. doi: 10.1007/s00424-022-02692-w. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Pflugers Arch. 2022. PMID: 35459955
-
Crystal structure of the cytoplasmic phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)-like region of Ciona intestinalis voltage-sensing phosphatase provides insight into substrate specificity and redox regulation of the phosphoinositide phosphatase activity.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 1;286(26):23368-77. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.214361. Epub 2011 May 4. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21543329 Free PMC article.
-
The structure of phosphoinositide phosphatases: Insights into substrate specificity and catalysis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jun;1851(6):698-710. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.09.015. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25264170 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bezanilla F. The voltage sensor in voltage-dependent ion channels. Physiol Rev. 2000;80:555–592. - PubMed
-
- Fukuda M, Kojima T, Kabayama H, Mikoshiba K. Mutation of the pleckstrin homology domain of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in immunodeficiency impaired inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate binding capacity. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:30303–30306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

