Clinicopathological concordance and discordance in three monozygotic twin pairs with familial Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 17615170
- PMCID: PMC2117553
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp.2006.113803
Clinicopathological concordance and discordance in three monozygotic twin pairs with familial Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
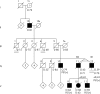
Aim: Neuropathological examination of both individuals in a monozygotic (MZ) twin pair with Alzheimer's disease (AD) is rare, especially in the molecular genetic era. We had the opportunity to assess the concordance and discordance of clinical presentation and neuropathology in three MZ twin pairs with AD.
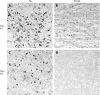
Methods: The MZ twins were identified and characterised by the University of Washington Alzheimer's Disease Research Center. We reviewed the available clinical and neuropathological records for all six cases looking specifically for concordance and discordance of clinical phenotype, neuritic amyloid plaques (NP), neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) and Lewy related pathology (LRP).
Results: Discordance in age of onset for developing AD in the MZ twins varied from 4 to 18 years. Clinical presentations also differed between twins. One twin presented with a dementia with Lewy Body clinical syndrome while the other presented with typical clinical AD. Neuropathology within the MZ twin pairs was concordant for NP and NFT, regardless of duration of disease, and was discordant for LRP. This difference was most marked in the late onset AD twin pair. One pair was found to have a mutation in presenilin-1 (PS1) (A79V) with remarkably late onset in a family member.
Conclusions: MZ twins with AD can vary considerably in age of onset, presentation and disease duration. The concordance of NP and NFT pathological change and the discordance of LRP support the concept that, in AD, the former are primarily under genetic control whereas the latter (LRP) is more influenced by disease duration and environmental factors. The A79V mutation in PS1 can be associated with very late onset of dementia.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
Comment in
-
Clinicopathological concordance and discordance in three monozygotic twin pairs with familial Alzheimer's disease.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007 Oct;78(10):1039. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2007.118562. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17878189 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Holmes C. Genotype and phenotype in Alzheimer's disease. Br J Psychiatry 2002180131–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous