Clinical features of X linked juvenile retinoschisis in Chinese families associated with novel mutations in the RS1 gene
- PMID: 17615541
- PMCID: PMC2768756
Clinical features of X linked juvenile retinoschisis in Chinese families associated with novel mutations in the RS1 gene
Abstract
Purpose: To describe the clinical phenotype of X linked juvenile retinoschisis (XLRS) in 12 Chinese families with 11 different mutations in the XLRS1 (RS1) gene.
Methods: Complete ophthalmic examinations were carried out in 29 affected males (12 probands), 38 heterozygous females carriers, and 100 controls. The coding regions of the RS1 gene that encodes retinoschisin were amplified by polymerase chain reaction and directly sequenced.
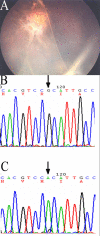
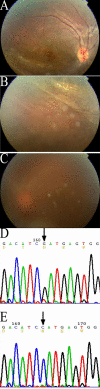
Results: Of the 29 male participants, 28 (96.6%) displayed typical foveal schisis. Eleven different RS1 mutations were identified in 12 families; four of these mutations, two frameshift mutations (26 del T of exon 1 and 488 del G of exon 5), and two missense mutations (Asp145His and Arg156Gly) of exon 5, had not been previously described. One non-disease-related polymorphism (NSP): 576C to T (Pro192Pro) change was also newly reported herein. We compared genotypes and observed more severe clinical features in families with the following mutations: frameshift mutation (26 del T) of exon 1, the splice donor site mutation (IVS1+2T to C),or Arg102Gln, Arg209His, and Arg213Gln mutations.
Conclusions: Severe XLRS phenotypes are associated with the frameshift mutation 26 del T, splice donor site mutation (IVS1+2T to C), and Arg102Gln, Asp145His, Arg209His, and Arg213Gln mutations. The wide variability in the phenotype in Chinese patients with XLRS and different mutations in the RS1 gene is described. Identification of mutations in the RS1 gene and expanded information on clinical manifestations will facilitate early diagnosis, appropriate early therapy, and genetic counseling regarding the prognosis of XLRS.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Novel mutations of the RS1 gene in a cohort of Chinese families with X-linked retinoschisis.Mol Vis. 2014 Jan 31;20:132-9. eCollection 2014. Mol Vis. 2014. PMID: 24505212 Free PMC article.
-
Novel XLRS1 gene mutations cause X-linked juvenile retinoschisis in Chinese families.Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2008 Jan-Feb;52(1):48-51. doi: 10.1007/s10384-007-0488-4. Epub 2008 Mar 28. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2008. PMID: 18369700
-
Truncation of retinoschisin protein associated with a novel splice site mutation in the RS1 gene.Mol Vis. 2008 Aug 25;14:1549-58. Mol Vis. 2008. PMID: 18728755 Free PMC article.
-
Of men and mice: Human X-linked retinoschisis and fidelity in mouse modeling.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2022 Mar;87:100999. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.100999. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 34390869 Review.
-
X-linked juvenile retinoschisis (XLRS): a review of genotype-phenotype relationships.Semin Ophthalmol. 2013 Sep-Nov;28(5-6):392-6. doi: 10.3109/08820538.2013.825299. Semin Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 24138048 Review.
Cited by
-
The gene mutation in a Taiwanese family with X-linked retinoschisis.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2015 Jun;31(6):309-14. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2015.03.001. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26043410 Free PMC article.
-
Novel mutations of the RS1 gene in a cohort of Chinese families with X-linked retinoschisis.Mol Vis. 2014 Jan 31;20:132-9. eCollection 2014. Mol Vis. 2014. PMID: 24505212 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical findings and RS1 genotype in 90 Chinese families with X-linked retinoschisis.Mol Vis. 2020 Apr 11;26:291-298. eCollection 2020. Mol Vis. 2020. PMID: 32300273 Free PMC article.
-
Four novel RS1 gene mutations in Polish patients with X-linked juvenile retinoschisis.Mol Vis. 2012;18:3004-12. Epub 2012 Dec 13. Mol Vis. 2012. PMID: 23288992 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding variable disease severity in X-linked retinoschisis: Does RS1 secretory mechanism determine disease severity?PLoS One. 2018 May 31;13(5):e0198086. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198086. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29851975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deutman AF. The hereditary dystrophies of the posterior pole of the eye. Netherlands: Van Gorcum; 1971. p.48-98.
-
- Tantri A, Vrabec TR, Cu-Unjieng A, Frost A, Annesley WH, Jr, Donoso LA. X-linked retinoschisis: a clinical and molecular genetic review. Surv Ophthalmol. 2004;49:214–30. - PubMed
-
- Mendoza-Londono R, Hiriyanna KT, Bingham EL, Rodriguez F, Shastry BS, Rodriguez A, Sieving PA, Tamayo ML. A Colombian family with X-linked juvenile retinoschisis with three affected females finding of a frameshift mutation. Ophthalmic Genet. 1999;20:37–43. - PubMed
-
- Sieving PA. Juvenile retinoschisis. In: Traboulsi E, editor. Genetic diseases of the eye. New York: Oxford University Press; 1998. p. 347-55.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
