Orally bioavailable potent soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors
- PMID: 17616115
- PMCID: PMC2596069
- DOI: 10.1021/jm070270t
Orally bioavailable potent soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors
Abstract
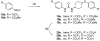
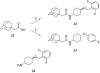
A series of N,N'-disubstituted ureas having a conformationally restricted cis- or trans-1,4-cyclohexane alpha to the urea were prepared and tested as soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibitors. This series of compounds showed low nanomolar to picomolar activities against recombinant human sEH. Both isomers showed similar potencies, but the trans isomers were more metabolically stable in human hepatic microsomes. Furthermore, these new potent inhibitors show a greater metabolic stability in vivo than previously described sEH inhibitors. We demonstrated that trans-4-[4-(3-adamantan-1-ylureido)cyclohexyloxy]benzoic acid 13g (t-AUCB, IC50 = 1.3 +/- 0.05 nM) had excellent oral bioavailability (98%, n = 2) and blood area under the curve in dogs and was effective in vivo to treat hypotension in lipopolysaccharide challenged murine models.
Figures




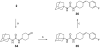


Similar articles
-
1,3-disubstituted ureas functionalized with ether groups are potent inhibitors of the soluble epoxide hydrolase with improved pharmacokinetic properties.J Med Chem. 2007 Oct 18;50(21):5217-26. doi: 10.1021/jm070705c. Epub 2007 Sep 26. J Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17894481 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic screening of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors in dogs.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2010 Jun 14;40(3):222-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2010.03.018. Epub 2010 Mar 30. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2010. PMID: 20359531 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic optimization of four soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors for use in a murine model of inflammation.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Jan;156(2):284-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2008.00009.x. Epub 2009 Jan 13. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19154430 Free PMC article.
-
Peptidyl-urea based inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolases.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006 Oct 15;16(20):5439-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.07.073. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006. PMID: 16908134 Free PMC article.
-
Meloxicam fails to augment the reno-protective effects of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats via increased 20-HETE levels.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2017 Sep;132:3-11. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2016.08.004. Epub 2016 Sep 3. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2017. PMID: 27596333 Review.
Cited by
-
Selection of Potent Inhibitors of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase for Usage in Veterinary Medicine.Front Vet Sci. 2020 Aug 26;7:580. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00580. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 33005645 Free PMC article.
-
Use of a soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor as an adjunctive analgesic in a horse with laminitis.Vet Anaesth Analg. 2013 Jul;40(4):440-8. doi: 10.1111/vaa.12030. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2013. PMID: 23463912 Free PMC article.
-
1-Trifluoromethoxyphenyl-3-(1-propionylpiperidin-4-yl) Urea, a Selective and Potent Dual Inhibitor of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase and p38 Kinase Intervenes in Alzheimer's Signaling in Human Nerve Cells.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019 Sep 18;10(9):4018-4030. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00271. Epub 2019 Aug 19. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31378059 Free PMC article.
-
Biological evaluation of a novel sorafenib analogue, t-CUPM.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;75(1):161-71. doi: 10.1007/s00280-014-2626-2. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25413440 Free PMC article.
-
Development of 1-((1,4-trans)-4-Aryloxycyclohexyl)-3-arylurea Activators of Heme-Regulated Inhibitor as Selective Activators of the Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2 Alpha (eIF2α) Phosphorylation Arm of the Integrated Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response.J Med Chem. 2017 Jul 13;60(13):5392-5406. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00059. Epub 2017 Jun 19. J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28590739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arand M, Grant DF, Beetham JK, Friedberg T, Oesch F, Hammock BD. Sequence similarity of mammalian epoxide hydrolases to the bacterial haloalkane dehalogenase and other related proteins. Implication for the potential catalytic mechanism of enzymatic epoxide hydrolysis. FEBS Lett. 1994;338:251–256. - PubMed
-
- Capdevila JH, Falck JR, Harris RC. Cytochrome P450 and arachidonic acid bioactivation: molecular and functional properties of the arachidonate monooxygenase. J. Lipid Res. 2000;41:163–181. - PubMed
- Fretland AJ, Omiecinski CJ. Epoxide hydrolases: biochemistry and molecular biology. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2000;129:41–59. - PubMed
- Meijer J, Depierre JW. Cytosolic epoxide hydrolase. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 1988;64:207–249. - PubMed
- Morisseau C, Hammock BD. Epoxide hydrolases: mechanisms, inhibitor designs, and biological roles. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2005;45:311–333. - PubMed
-
- Zeldin DC. Epoxygenase Pathways of Arachidonic Acid Metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:36059–36062. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe H, Vriens J, Prenen J, Droogmans G, Voets T, Nilius B. Anandamide and arachidonic acid use epoxyeicosatrienoic acids to activate TRPV4 channels. Nature. 2003;424:434–438. - PubMed
- Earley S, Heppner TJ, Nelson MT, Brayden JE. TRPV4 forms a novel Ca2+ signaling complex with ryanodine receptors and BKCa channels. Circ. Res. 2005;97:1270–1279. - PubMed
- Vriens J, Owsianik G, Fisslthaler B, Suzuki M, Janssens A, Voets T, Morisseau C, Hammock BD, Fleming I, Busse R, Nilius B. Modulation of the Ca2+ permeable cation channel TRPV4 by cytochrome P450 epoxygenases in vascular endothelium. Circ. Res. 2005;97:908–915. - PubMed
-
- Spiecker M, Liao J. Vascular protective effects of cytochrome p450 epoxygenase-derived eicosanoids. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005;433:413–420. - PubMed
- Node K, Huo Y, Ruan X, Yang B, Spiecker M, Ley K, Zeldin DC, Liao JK. Anti-inflammatory properties of cytochrome P450 epoxygenase-derived eicosanoids. Science. 1999;285:1276–1279. - PMC - PubMed
- Liu Y, Zhang Y, Schmelzer K, Lee T-S, Fang X, Zhu Y, Spector AA, Gill S, Morisseau C, Hammock BD, Shyy JY-J. The antiinflammatory effect of laminar flow: The role of ΠΠAPγ, epoxyeicosatrienoic acids, and soluble epoxide hydrolase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005;102:16747–16752. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

