Chemical genetic identification of glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase as the target for a novel bleaching herbicide in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 17616508
- PMCID: PMC1914136
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.107.099705
Chemical genetic identification of glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase as the target for a novel bleaching herbicide in Arabidopsis
Abstract
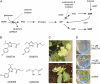
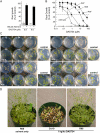
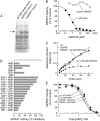
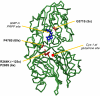
A novel phenyltriazole acetic acid compound (DAS734) produced bleaching of new growth on a variety of dicotyledonous weeds and was a potent inhibitor of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) seedling growth. The phytotoxic effects of DAS734 on Arabidopsis were completely alleviated by addition of adenine to the growth media. A screen of ethylmethanesulfonate-mutagenized Arabidopsis seedlings recovered seven lines with resistance levels to DAS734 ranging from 5- to 125-fold. Genetic tests determined that all the resistance mutations were dominant and allelic. One mutation was mapped to an interval on chromosome 4 containing At4g34740, which encodes an isoform of glutamine phosphoribosylamidotransferase (AtGPRAT2), the first enzyme of the purine biosynthetic pathway. Sequencing of At4g34740 from the resistant lines showed that all seven contained mutations producing changes in the encoded polypeptide sequence. Two lines with the highest level of resistance (125-fold) contained the mutation R264K. The wild-type and mutant AtGPRAT2 enzymes were cloned and functionally overexpressed in Escherichia coli. Assays of the recombinant enzyme showed that DAS734 was a potent, slow-binding inhibitor of the wild-type enzyme (I(50) approximately 0.2 microm), whereas the mutant enzyme R264K was not significantly inhibited by 200 microm DAS734. Another GPRAT isoform in Arabidopsis, AtGPRAT3, was also inhibited by DAS734. This combination of chemical, genetic, and biochemical evidence indicates that the phytotoxicity of DAS734 arises from direct inhibition of GPRAT and establishes its utility as a new and specific chemical genetic probe of plant purine biosynthesis. The effects of this novel GPRAT inhibitor are compared to the phenotypes of known AtGPRAT genetic mutants.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Crystal Structure of the Chloroplastic Glutamine Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate Amidotransferase GPRAT2 From Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Feb 27;11:157. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00157. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32174940 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Arabidopsis thaliana variants with differential glyphosate responses.J Plant Physiol. 2007 Oct;164(10):1337-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2006.08.008. Epub 2006 Oct 30. J Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17074412
-
Inhibition profile of trifludimoxazin towards PPO2 target site mutations.Pest Manag Sci. 2023 Feb;79(2):507-519. doi: 10.1002/ps.7216. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Pest Manag Sci. 2023. PMID: 36178376 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to AHAS inhibitor herbicides: current understanding.Pest Manag Sci. 2014 Sep;70(9):1340-50. doi: 10.1002/ps.3710. Epub 2014 Jan 20. Pest Manag Sci. 2014. PMID: 24338926 Review.
-
Understanding paraquat resistance mechanisms in Arabidopsis thaliana to facilitate the development of paraquat-resistant crops.Plant Commun. 2022 May 9;3(3):100321. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2022.100321. Epub 2022 Mar 25. Plant Commun. 2022. PMID: 35576161 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Opportunities and challenges in plant chemical biology.Nat Chem Biol. 2009 May;5(5):268-72. doi: 10.1038/nchembio0509-268. Nat Chem Biol. 2009. PMID: 19377447 No abstract available.
-
Considerations for designing chemical screening strategies in plant biology.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Apr 8;6:131. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00131. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 25904921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A chemical inhibitor of jasmonate signaling targets JAR1 in Arabidopsis thaliana.Nat Chem Biol. 2014 Oct;10(10):830-6. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1591. Epub 2014 Aug 17. Nat Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 25129030
-
Powerful partners: Arabidopsis and chemical genomics.Arabidopsis Book. 2009;7:e0109. doi: 10.1199/tab.0109. Epub 2009 Jan 21. Arabidopsis Book. 2009. PMID: 22303245 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal Structure of the Chloroplastic Glutamine Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate Amidotransferase GPRAT2 From Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Feb 27;11:157. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00157. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32174940 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asami T, Nakano T, Nakashita H, Sekimata K, Shimada Y, Yoshida S (2003) The influence of chemical genetics on plant science: shedding light on functions and mechanism of action of brassinosteroids using biosynthesis inhibitors. J Plant Growth Regul 22 336–349 - PubMed
-
- Ashihara H, Stasolla C, Loukanina N, Thorpe TA (2000) Purine and pyrimidine metabolism in cultured white spruce (Picea glauca) cells: metabolic fate of 14C-labeled precursors and activity of key enzymes. Physiol Plant 108 25–33
-
- Ashihara H, Stasolla C, Loukanina N, Thorpe TA (2001) Purine metabolism during white spruce somatic embryo development: salvage of adenine, adenosine, and inosine. Plant Sci 160 647–657 - PubMed
-
- Bera AK, Chen S, Smith JL, Zalkin H (1999) Interdomain signaling in glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase. J Biol Chem 274 36498–36504 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

