A more efficient RNAi inducible system for tight regulation of gene expression in mammalian cells and xenograft animals
- PMID: 17616554
- PMCID: PMC1924899
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.520707
A more efficient RNAi inducible system for tight regulation of gene expression in mammalian cells and xenograft animals
Abstract
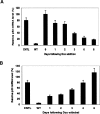
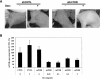
Two types of tetracycline-controlled inducible RNAi expression systems have been developed that generally utilize multiple tetracycline operators (TetOs) or repressor fusion proteins to overcome the siRNA leakiness. Here, we report a novel system that overexpresses the tetracycline repressor (TetR) via a bicistronic construct to control siRNA expression. The high level of TetR expression ensures that the inducible promoter is tightly bound, with minimal basal transcription, allowing for regulation solely dependent on TetR rather than a TetR fusion protein via a more complicated mechanism. At the same time, this system contains only a single TetO, thus minimizing the promoter impairment occurring in existing systems due to the incorporation of multiple TetOs, and maximizing the siRNA expression upon induction. In addition, this system combines all the components required for regulation of siRNA expression into a single lentiviral vector, so that stable cell lines can be generated by a single transduction and selection, with significant reduction in time and cost. Taken together, this all-in-one lentiviral vector with the feature of TetR overexpression provides a unique and more efficient tool for conditional gene knockdown that has wide applications. We have demonstrated the high degree of robustness and versatility of this system as applied to several mammalian cells and xenograft animals.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A tightly regulated and reversibly inducible siRNA expression system for conditional RNAi-mediated gene silencing in mammalian cells.J Gene Med. 2007 Jul;9(7):620-34. doi: 10.1002/jgm.1048. J Gene Med. 2007. PMID: 17486668
-
Design and in vitro characterization of a single regulatory module for efficient control of gene expression in both plasmid DNA and a self-inactivating lentiviral vector.Mol Med. 2001 Aug;7(8):569-79. Mol Med. 2001. PMID: 11591893 Free PMC article.
-
A versatile tool for conditional gene expression and knockdown.Nat Methods. 2006 Feb;3(2):109-16. doi: 10.1038/nmeth846. Nat Methods. 2006. PMID: 16432520
-
Vector-based RNAi approaches for stable, inducible and genome-wide screens.Drug Discov Today. 2006 Nov;11(21-22):975-82. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2006.09.008. Epub 2006 Sep 26. Drug Discov Today. 2006. PMID: 17055406 Review.
-
Small-molecule inducible transcriptional control in mammalian cells.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2020 Dec;40(8):1131-1150. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2020.1808583. Epub 2020 Aug 30. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32862714 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transferring a synthetic gene circuit from yeast to mammalian cells.Nat Commun. 2013;4:1451. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2471. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 23385595 Free PMC article.
-
Strand antagonism in RNAi: an explanation of differences in potency between intracellularly expressed siRNA and shRNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Feb;40(4):1797-806. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr927. Epub 2011 Oct 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22039150 Free PMC article.
-
The construction of siRNA plasmid targeting mouse HIF-1alpha and in vitro study of its inhibition effect.Neurosci Bull. 2009 Jun;25(3):122-30. doi: 10.1007/s12264-009-8122-8. Neurosci Bull. 2009. PMID: 19448686 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated expression of AKR1C3 increases resistance of cancer cells to ionizing radiation via modulation of oxidative stress.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 24;9(11):e111911. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111911. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25419901 Free PMC article.
-
c-Met targeting enhances the effect of irradiation and chemical agents against malignant colon cells harboring a KRAS mutation.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 26;9(11):e113186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113186. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25427200 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
