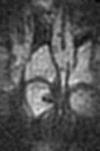
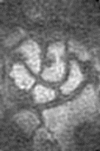
A modification of the Omeract RA MRI score for erosions for use with an extremity MRI system with reduced field of view
- PMID: 17616555
- PMCID: PMC2095331
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2007.072561
A modification of the Omeract RA MRI score for erosions for use with an extremity MRI system with reduced field of view
Abstract
Objectives: To develop and test the reliability of a modified version of the OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging score (RAMRIS) for erosions using extremity MRI (eMRI) with reduced field of view (RAMRIS-RV).
Methods: Using a MagneVu 0.2 T machine, the preliminary RAMRIS-RV assessed erosions in metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints 2-3, bases of metacarpal (MC) 2-5, and all wrist bones excluding base MC 1, pisiform and trapezium. T1 weighted images of >/=500 MCP and wrist bony sites from a mixed severity RA and control cohort were evaluated. An inter-reader reliability study evaluating 300 wrist and 160 MCP bony sites was then performed.
Results: Mean per cent exact (and close) agreement results were as follows: MCP proximal sites 83.5 (96.2), MCP distal 54.4 (77.2), bases MC 2-4 85.2 (96.7), carpal bones 79.0 (92.1), distal radius/ulna 66.4 (87.8). The base of MCP 5 was visualised in </=50% cases (13/25) and was removed from the final RAMRIS-RV.
Conclusions: The RAMRIS-RV is a practical tool that can be used with eMRI with a reduced field of view. This study shows excellent inter-reader reliability for erosion assessment, albeit in a reduced number of bony sites.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Similar articles
-
Detection of rheumatoid arthritis bone erosions by two different dedicated extremity MRI units and conventional radiography.Ann Rheum Dis. 2008 Jul;67(7):998-1003. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.076026. Epub 2007 Nov 5. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. PMID: 17984195
-
Patterns of magnetic resonance imaging bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis--which bones are most frequently involved and show the most change?J Rheumatol. 2011 Sep;38(9):2014-7. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.110416. J Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21885509
-
The OMERACT-RAMRIS rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging joint space narrowing score: intrareader and interreader reliability and agreement with computed tomography and conventional radiography.J Rheumatol. 2014 Feb;41(2):392-7. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.131087. Epub 2013 Dec 1. J Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24293568
-
OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Core set of MRI acquisitions, joint pathology definitions, and the OMERACT RA-MRI scoring system.J Rheumatol. 2003 Jun;30(6):1385-6. J Rheumatol. 2003. PMID: 12784422 Review.
-
OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Summary of OMERACT 6 MR Imaging Module.J Rheumatol. 2003 Jun;30(6):1387-92. J Rheumatol. 2003. PMID: 12784423 Review.
Cited by
-
A comparison of dedicated 1.0 T extremity MRI vs large-bore 1.5 T MRI for semiquantitative whole organ assessment of osteoarthritis: the MOST study.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010 Feb;18(2):168-74. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2009.08.017. Epub 2009 Sep 9. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010. PMID: 19766580 Free PMC article.
-
[Low-field magnetic resonance imaging for rheumatoid arthritis].Z Rheumatol. 2010 Feb;69(1):79-86. doi: 10.1007/s00393-009-0547-y. Z Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 19894053 German.
References
-
- Dohn U M, Ejbjerg B J, Court‐Payen M, Hasselquist M, Narvestad E, Szkudlarek M.et al Are bone erosions detected by magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasonography true erosions? A comparison with computed tomography in rheumatoid arthritis metacarpophalangeal joints. Arthritis Res Ther 20068R110 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cohen S, Deodhar A, Kavanaugh A, Potter H H, Ruderman E, Shmerling R H.et al for the American College of Rheumatology Extremity Magnetic Resonance Imaging Task Force. Extremity magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: report of the American College of Rheumatology Extremity Magnetic Resonance Imaging Task Force. Arthritis Rheum 2006541034–1047. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous