Rcs and PhoPQ regulatory overlap in the control of Salmonella enterica virulence
- PMID: 17616593
- PMCID: PMC2045174
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00640-07
Rcs and PhoPQ regulatory overlap in the control of Salmonella enterica virulence
Abstract
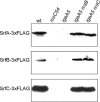
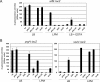
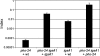
Genetic screens based on the use of MudJ-generated lac fusions permitted the identification of novel genes regulated by the Rcs signal transduction system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Besides genes that are also found in the Escherichia coli genome, our screens identified Salmonella-specific genes regulated by RcsB, including bapA, siiE, srfA, and srfB. Here we show that the srfABC operon is negatively regulated by RcsB and by PhoP. In vivo studies using mutants with constitutive activation of the Rcs and/or PhoPQ system suggested that there is an overlap between these regulatory systems in the control of Salmonella virulence.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PhoP/Q regulated genes in Salmonella typhi identification of melittin sensitive mutants.Microb Pathog. 1997 Mar;22(3):165-79. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1996.0099. Microb Pathog. 1997. PMID: 9075219
-
Activation of the RcsC/YojN/RcsB phosphorelay system attenuates Salmonella virulence.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Oct;54(2):386-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04293.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15469511
-
Repression of the RcsC-YojN-RcsB phosphorelay by the IgaA protein is a requisite for Salmonella virulence.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Sep;53(5):1437-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04213.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15387821
-
The ins and outs of virulence gene expression: Mg2+ as a regulatory signal.Bioessays. 1998 Jan;20(1):96-101. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199801)20:1<96::AID-BIES13>3.0.CO;2-3. Bioessays. 1998. PMID: 9504051 Review.
-
Adaptation to the host environment: regulation of the SPI1 type III secretion system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007 Feb;10(1):24-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.12.002. Epub 2007 Jan 5. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17208038 Review.
Cited by
-
The Rational Design, Synthesis, and Antimicrobial Properties of Thiophene Derivatives That Inhibit Bacterial Histidine Kinases.J Med Chem. 2016 Oct 13;59(19):8830-8847. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00580. Epub 2016 Sep 26. J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27575438 Free PMC article.
-
Role of OB-Fold Protein YdeI in Stress Response and Virulence of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis.J Bacteriol. 2020 Dec 7;203(1):e00237-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00237-20. Print 2020 Dec 7. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 33106344 Free PMC article.
-
Draft genomes of Cronobacter sakazakii strains isolated from dried spices bring unique insights into the diversity of plant-associated strains.Stand Genomic Sci. 2018 Nov 29;13:35. doi: 10.1186/s40793-018-0339-6. eCollection 2018. Stand Genomic Sci. 2018. PMID: 30519380 Free PMC article.
-
A Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi plasmid induces rapid and massive apoptosis in infected macrophages.Cell Mol Immunol. 2010 Jul;7(4):271-8. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2010.17. Epub 2010 May 17. Cell Mol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20473323 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Effect of SlyA on rcsB Expression in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2019 Jan 28;201(4):e00673-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00673-18. Print 2019 Feb 15. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30510144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arricau, N., D. Hermant, H. Waxin, C. Ecobichon, P. S. Duffey, and M. Y. Popoff. 1998. The RcsB-RcsC regulatory system of Salmonella typhi differentially modulates the expression of invasion proteins, flagellin and Vi antigen in response to osmolarity. Mol. Microbiol. 29:835-850. - PubMed
-
- Beier, D., and R. Gross. 2006. Regulation of bacterial virulence by two-component systems. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 9:143-152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

