Rcs and PhoPQ regulatory overlap in the control of Salmonella enterica virulence
- PMID: 17616593
- PMCID: PMC2045174
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00640-07
Rcs and PhoPQ regulatory overlap in the control of Salmonella enterica virulence
Abstract
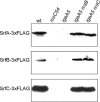
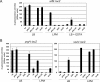
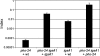
Genetic screens based on the use of MudJ-generated lac fusions permitted the identification of novel genes regulated by the Rcs signal transduction system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Besides genes that are also found in the Escherichia coli genome, our screens identified Salmonella-specific genes regulated by RcsB, including bapA, siiE, srfA, and srfB. Here we show that the srfABC operon is negatively regulated by RcsB and by PhoP. In vivo studies using mutants with constitutive activation of the Rcs and/or PhoPQ system suggested that there is an overlap between these regulatory systems in the control of Salmonella virulence.
Figures


References
-
- Arricau, N., D. Hermant, H. Waxin, C. Ecobichon, P. S. Duffey, and M. Y. Popoff. 1998. The RcsB-RcsC regulatory system of Salmonella typhi differentially modulates the expression of invasion proteins, flagellin and Vi antigen in response to osmolarity. Mol. Microbiol. 29:835-850. - PubMed
-
- Beier, D., and R. Gross. 2006. Regulation of bacterial virulence by two-component systems. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 9:143-152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

