Negative regulation of the EcoRI restriction enzyme gene is associated with intragenic reverse promoters
- PMID: 17616602
- PMCID: PMC2045195
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00127-07
Negative regulation of the EcoRI restriction enzyme gene is associated with intragenic reverse promoters
Abstract
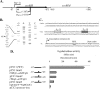
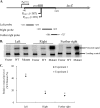
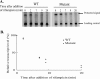
Type II restriction-modification systems are expected to possess mechanisms for tight regulation of their expression to suppress the potential of lethal attack on their host bacteria when they establish and maintain themselves within them. Although the EcoRI restriction enzyme has been well characterized, regulation of its expression is still poorly understood. In this study, mutational analysis with lacZ gene fusion and primer extension assay identified a promoter for the transcription of the ecoRIR gene. Further analyses revealed that an intragenic region containing two overlapping reverse promoter-like elements acted as a negative regulator for ecoRIR gene expression. The activity of these putative reverse promoters was verified by transcriptional gene fusion, primer extension and in vitro transcription. Mutations in these reverse promoters resulted in increased gene expression in both translational and transcriptional gene fusions. An RNase protection assay revealed that the transcript level of the wild type relative to that of the reverse promoter mutant at the downstream regions was much lower than the level at the upstream regions. This suggests that these reverse promoter-like elements affect their downstream transcript level. The possible mechanisms of this kind of negative regulation, in addition to their possible biological roles, are discussed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of the EcoRI restriction-modification system: Identification of ecoRIM gene promoters and their upstream negative regulators in the ecoRIR gene.Gene. 2007 Oct 1;400(1-2):140-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2007.06.006. Epub 2007 Jun 14. Gene. 2007. PMID: 17618069
-
Transcriptional regulation of the orf19 gene and the tir-cesT-eae operon of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2001 May;183(9):2823-33. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.9.2823-2833.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11292802 Free PMC article.
-
Activation from a distance: roles of Lrp and integration host factor in transcriptional activation of gltBDF.J Bacteriol. 2001 Jul;183(13):3910-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.13.3910-3918.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11395454 Free PMC article.
-
Closely spaced and divergent promoters for an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase gene and a tRNA operon in Escherichia coli. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gltX, valU and alaW.J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 20;214(4):845-64. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90340-R. J Mol Biol. 1990. PMID: 2201777
-
Cloning, DNA sequence, functional analysis and transcriptional regulation of the genes encoding dipicolinic acid synthetase required for sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.J Mol Biol. 1993 Jul 20;232(2):468-83. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1403. J Mol Biol. 1993. PMID: 8345520
Cited by
-
Highlights of the DNA cutters: a short history of the restriction enzymes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jan;42(1):3-19. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt990. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24141096 Free PMC article.
-
Low-level expression of the Type II restriction-modification system confers potent bacteriophage resistance in Escherichia coli.DNA Res. 2020 Feb 1;27(1):dsaa003. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsaa003. DNA Res. 2020. PMID: 32167561 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time kinetics of restriction-modification gene expression after entry into a new host cell.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 May;36(8):2581-93. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn097. Epub 2008 Mar 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18334533 Free PMC article.
-
Maintenance forced by a restriction-modification system can be modulated by a region in its modification enzyme not essential for methyltransferase activity.J Bacteriol. 2008 Mar;190(6):2039-49. doi: 10.1128/JB.01319-07. Epub 2008 Jan 11. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18192396 Free PMC article.
-
Topologies of synthetic gene circuit for optimal fold change activation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 May 21;49(9):5393-5406. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab253. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34009384 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alvarez, M. A., K. F. Chater, and M. R. Rodicio. 1993. Complex transcription of an operon encoding the SalI restriction-modification system of Streptomyces albus G. Mol. Microbiol. 8:243-252. - PubMed
-
- Becker, A., A. Kleickmann, M. Keller, W. Arnold, and A. Puhler. 1993. Identification and analysis of the Rhizobium meliloti exoAMONP genes involved in exopolysaccharide biosynthesis and mapping of promoters located on the exoHKLAMONP fragment. Mol. Gen. Genet. 241:367-379. - PubMed
-
- Betlach, M., V. Hershfield, L. Chow, W. Brown, H. Goodman, and H. W. Boyer. 1976. A restriction endonuclease analysis of the bacterial plasmid controlling the EcoRI restriction and modification of DNA. Fed. Proc. 35:2037-2043. - PubMed
-
- Brantl, S. 2002. Antisense-RNA regulation and RNA interference. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1575:15-25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

