MYC2 differentially modulates diverse jasmonate-dependent functions in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 17616737
- PMCID: PMC1955694
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.106.048017
MYC2 differentially modulates diverse jasmonate-dependent functions in Arabidopsis
Abstract
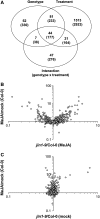
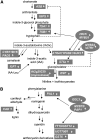
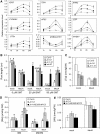
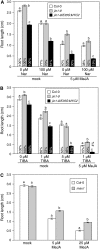
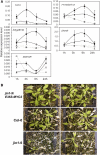
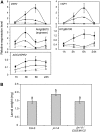
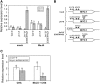
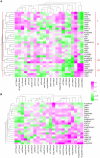
The Arabidopsis thaliana basic helix-loop-helix Leu zipper transcription factor (TF) MYC2/JIN1 differentially regulates jasmonate (JA)-responsive pathogen defense (e.g., PDF1.2) and wound response (e.g., VSP) genes. In this study, genome-wide transcriptional profiling of wild type and mutant myc2/jin1 plants followed by functional analyses has revealed new roles for MYC2 in the modulation of diverse JA functions. We found that MYC2 negatively regulates Trp and Trp-derived secondary metabolism such as indole glucosinolate biosynthesis during JA signaling. Furthermore, MYC2 positively regulates JA-mediated resistance to insect pests, such as Helicoverpa armigera, and tolerance to oxidative stress, possibly via enhanced ascorbate redox cycling and flavonoid biosynthesis. Analyses of MYC2 cis binding elements and expression of MYC2-regulated genes in T-DNA insertion lines of a subset of MYC2-regulated TFs suggested that MYC2 might modulate JA responses via differential regulation of an intermediate spectrum of TFs with activating or repressing roles in JA signaling. MYC2 also negatively regulates its own expression, and this may be one of the mechanisms used in fine-tuning JA signaling. Overall, these results provide new insights into the function of MYC2 and the transcriptional coordination of the JA signaling pathway.
Figures

References
-
- Alonso, J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301 653–657. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, J.P., Badruzsaufari, E., Schenk, P.M., Manners, J.M., Desmond, O.J., Ehlert, C., Maclean, D.J., Ebert, P.R., and Kazan, K. (2004). Antagonistic interaction between abscisic acid and jasmonate-ethylene signaling pathways modulates defense gene expression and disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16 3460–3479. - PMC - PubMed
NOTE ADDED IN PROOF
-
- Nafisi et al. (2007) recently showed that CYP71A13 catalyzes the conversion of indole-3-acetaldoxime in camalexin synthesis. MYC2 negatively regulates CYP71A13 (see Supplemental Table 1 online), providing additional evidence that MYC2 is a negative regulator of JA-dependent camalexin synthesis in Arabidopsis.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

