DNA damage, homology-directed repair, and DNA methylation
- PMID: 17616978
- PMCID: PMC1913100
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030110
DNA damage, homology-directed repair, and DNA methylation
Erratum in
-
Correction: DNA Damage, Homology-Directed Repair, and DNA Methylation.PLoS Genet. 2017 Feb 10;13(2):e1006605. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006605. eCollection 2017 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28187196 Free PMC article.
Abstract
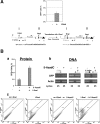
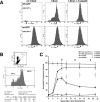
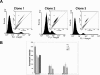
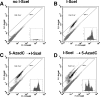
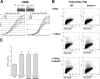
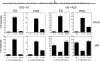
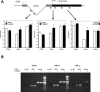
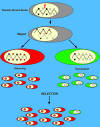
To explore the link between DNA damage and gene silencing, we induced a DNA double-strand break in the genome of Hela or mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells using I-SceI restriction endonuclease. The I-SceI site lies within one copy of two inactivated tandem repeated green fluorescent protein (GFP) genes (DR-GFP). A total of 2%-4% of the cells generated a functional GFP by homology-directed repair (HR) and gene conversion. However, approximately 50% of these recombinants expressed GFP poorly. Silencing was rapid and associated with HR and DNA methylation of the recombinant gene, since it was prevented in Hela cells by 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine. ES cells deficient in DNA methyl transferase 1 yielded as many recombinants as wild-type cells, but most of these recombinants expressed GFP robustly. Half of the HR DNA molecules were de novo methylated, principally downstream to the double-strand break, and half were undermethylated relative to the uncut DNA. Methylation of the repaired gene was independent of the methylation status of the converting template. The methylation pattern of recombinant molecules derived from pools of cells carrying DR-GFP at different loci, or from an individual clone carrying DR-GFP at a single locus, was comparable. ClustalW analysis of the sequenced GFP molecules in Hela and ES cells distinguished recombinant and nonrecombinant DNA solely on the basis of their methylation profile and indicated that HR superimposed novel methylation profiles on top of the old patterns. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and RNA analysis revealed that DNA methyl transferase 1 was bound specifically to HR GFP DNA and that methylation of the repaired segment contributed to the silencing of GFP expression. Taken together, our data support a mechanistic link between HR and DNA methylation and suggest that DNA methylation in eukaryotes marks homologous recombined segments.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
GADD45α inhibition of DNMT1 dependent DNA methylation during homology directed DNA repair.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Mar;40(6):2481-93. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1115. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22135303 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted DNA methylation by homology-directed repair in mammalian cells. Transcription reshapes methylation on the repaired gene.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jan;42(2):804-21. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt920. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24137009 Free PMC article.
-
Double strand breaks can initiate gene silencing and SIRT1-dependent onset of DNA methylation in an exogenous promoter CpG island.PLoS Genet. 2008 Aug 15;4(8):e1000155. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000155. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18704159 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation and cancer therapy.Drug Resist Updat. 2003 Dec;6(6):341-53. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2003.10.002. Drug Resist Updat. 2003. PMID: 14744498 Review.
-
DNA methylation and carcinogenesis.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2001 Mar;66(3):235-55. doi: 10.1023/a:1010249510906. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2001. PMID: 11333147 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of DNA Methyltransferase Recruitment in Mammals.Genes (Basel). 2018 Dec 10;9(12):617. doi: 10.3390/genes9120617. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30544749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High preservation of CpG cytosine methylation patterns at imprinted gene loci in liver and brain of aged mice.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 9;8(9):e73496. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073496. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24039963 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of epigenetic modifiers in repair of DNA damage associated with chronic inflammatory diseases.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2019 Apr-Jun;780:69-81. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2017.09.005. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2019. PMID: 31395351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation and DNA damage: cause, effect or both.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023 Apr;19(4):200-211. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00905-1. Epub 2023 Feb 7. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36750681 Review.
-
Stimulation of homology-directed repair at I-SceI-induced DNA breaks during the permissive life cycle of human cytomegalovirus.J Virol. 2011 Jun;85(12):6049-54. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02514-10. Epub 2011 Apr 13. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21490102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li E, Bestor TH, Jaenisch R. Targeted mutation of the DNA methyltransferase gene results in embryonic lethality. Cell. 1992;69:915–926. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

