VDAC closure increases calcium ion flux
- PMID: 17617374
- PMCID: PMC2220155
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.06.002
VDAC closure increases calcium ion flux
Abstract
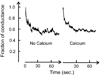
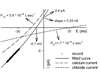
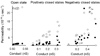
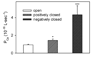
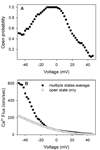
VDAC is the major permeability pathway in the mitochondrial outer membrane and can control the flow of metabolites and ions. Therefore Ca(2+) flux across the outer membrane occurs mainly through VDAC. Since both Ca(2+) fluxes and VDAC are involved in apoptosis, we examined whether Ca(2+) is required for channel formation by VDAC isolated from rat liver. The voltage gating of VDAC does not require Ca(2+) and it functions normally with or without Ca(2+). Additionally, VDAC generally shows a higher permeability to Ca(2+) in the closed states (states with lower permeability to metabolites) than that in the open state. Thus VDAC closure, which induces apoptosis, also favors Ca(2+) flux into mitochondria, which can also lead to permeability transition and cell death. These results are consistent with the view that VDAC closure is a pro-apoptotic signal.
Figures
References
-
- Tan W, Lai JC, Miller P, Stein CA, Colombini M. Phosphorothioate oligonucleotides reduce mitochondrial outer membrane permeability to ADP. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006;292:C1388–C1397. - PubMed
-
- Krauskopf A, Eriksson O, Craigen WJ, Forte MA, Bernardi P. Properties of the permeability transition in VDAC1(−/−) mitochondria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2006;1757:590–595. - PubMed
-
- Colombini M. Structure and mode of action of a voltage-dependent anion-selective channel (VDAC) located in the outer mitochondrial membrane. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 1980;341:552–563. - PubMed
-
- Hodge T, Colombini M. Regulation of metabolite flux through voltage-gating of VDAC channels. J. Membr. Biol. 1987;157:271–279. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

