Evidence for sugar addiction: behavioral and neurochemical effects of intermittent, excessive sugar intake
- PMID: 17617461
- PMCID: PMC2235907
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2007.04.019
Evidence for sugar addiction: behavioral and neurochemical effects of intermittent, excessive sugar intake
Abstract
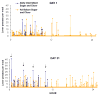
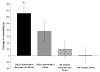
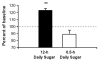
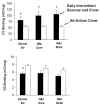
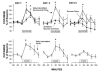
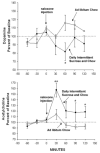
[Avena, N.M., Rada, P., Hoebel B.G., 2007. Evidence for sugar addiction: Behavioral and neurochemical effects of intermittent, excessive sugar intake. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews XX(X), XXX-XXX]. The experimental question is whether or not sugar can be a substance of abuse and lead to a natural form of addiction. "Food addiction" seems plausible because brain pathways that evolved to respond to natural rewards are also activated by addictive drugs. Sugar is noteworthy as a substance that releases opioids and dopamine and thus might be expected to have addictive potential. This review summarizes evidence of sugar dependence in an animal model. Four components of addiction are analyzed. "Bingeing," "withdrawal," "craving" and "cross-sensitization" are each given operational definitions and demonstrated behaviorally with sugar bingeing as the reinforcer. These behaviors are then related to neurochemical changes in the brain that also occur with addictive drugs. Neural adaptations include changes in dopamine and opioid receptor binding, enkephalin mRNA expression and dopamine and acetylcholine release in the nucleus accumbens. The evidence supports the hypothesis that under certain circumstances rats can become sugar dependent. This may translate to some human conditions as suggested by the literature on eating disorders and obesity.
Figures
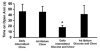
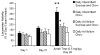
References
-
- Acquas E, Carboni E, Di Chiara G. Profound depression of mesolimbic dopamine release after morphine withdrawal in dependent rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991;193:133–134. - PubMed
-
- Acquas E, Di Chiara G. Depression of mesolimbic dopamine transmission and sensitization to morphine during opiate abstinence. J Neurochem. 1992;58:1620–1625. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed SH, Koob GF. Transition from moderate to excessive drug intake: change in hedonic set point. Science. 1998;282:298–300. - PubMed
-
- Alburges ME, Narang N, Wamsley JK. Alterations in the dopaminergic receptor system after chronic administration of cocaine. Synapse. 1993;14:314–323. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders Fouth Edition Text Revision (DSM-IV-TR) American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC: 2000.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

