Biomarkers of oxidative stress and heavy metal levels as indicators of environmental pollution in African cat fish (Clarias gariepinus) from Nigeria Ogun River
- PMID: 17617680
- PMCID: PMC3728582
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph2007040011
Biomarkers of oxidative stress and heavy metal levels as indicators of environmental pollution in African cat fish (Clarias gariepinus) from Nigeria Ogun River
Abstract
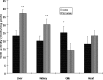
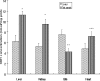
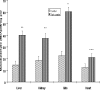
Levels of Zn, Cu, Cd, As, and Pb in the kidney, Liver, Gills and Heart of African cat fish (Clarias gariepinus) from the Ogun River in Ogun State located close to six major industries in the South Western part of Nigeria, were determined using Bulk Scientific Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer. Fishes were also collected from Government owned fish farm in Agodi, Ibadan which was considered a reference site. The activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione S-transferase (GST), glutathione (GSH) concentration and malondialdehyde (MDA) formation were also determined. The trend of accumulation of the metals in the organs is as follows: Heart - Zn > Cu > Pb > As > Cd; Gills - Zn > Cu > Pb > Cd > As; Kidney - Zn > Cu > Pb > As > Cd; Liver - Zn > Cu > Pb > As > Cd. The order of concentration of the metals in the organs is as follows: Arsenite - Kidney > Liver > Gills > Heart; Zinc - Gills > Liver > Kidney > Heart; Lead- Liver > Kidney > Gills > Heart; Copper- Kidney > Liver > Gills > Heart; Cadmium > Liver > Gills > Kidney > Heart. The levels of heavy metals ranged between 0.25- 8.96 ppm in the heart, 0.69- 19.05 ppm in the kidneys, 2.10-19.75 ppm in the liver and 1.95-20.35 ppm in the gills. SOD activity increased by 61% in the liver, 50% in the kidney and in the heart by 28 % while a significant decrease (44%) was observed in the gill of Clarias gariepinus from Ogun river compared to that Agodi fish farm (P<0.001). On the contrary there was 46%, 41%, 50% and 19% decrease in CAT activity in the liver, kidney, gills and heart respectively. The levels of GST activities in the liver, kidney and heart of Clarias gariepinus from Ogun river increased by 62%, 72% and 37% respectively (P<0.001) whereas there was a significant decrease (41%) in the gills (P<0.05) compared to that from the Agodi fish farm. GSH concentration increased by 81%, 83% and 53% in the liver, kidney and heart respectively but decreased by 44% in the gills. MDA levels of Clarias gariepinus were significantly (P<0.001) elevated in the liver, kidney, gills and heart by 177%, 102%, 168% and 71% respectively compared to that from Agodi fish farm. Overall, the results demonstrate that alteration in the antioxidant enzymes, glutathione system and induction of lipid peroxidation reflects the presence of heavy metals which may cause oxidative stress in the Clarias gariepinus from Ogun River. The study therefore provides a rational use of biomarkers of oxidative stress in biomonitoring of aquatic pollution.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Heavy metal bioaccumulation, oxidative stress and genotoxicity in African catfish Clarias gariepinus from Orontes river.Ecotoxicology. 2020 Nov;29(9):1522-1537. doi: 10.1007/s10646-020-02253-w. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Ecotoxicology. 2020. PMID: 32710163
-
Histopatological alterations and oxidative stress in liver and kidney of Leuciscus cephalus following exposure to heavy metals in the Tur River, North Western Romania.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2015 Sep;119:198-205. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.05.029. Epub 2015 May 25. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2015. PMID: 26005919
-
Toxicological Assessment of Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers In Clarias gariepinus from Igbokoda River of South Western Nigeria.Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2018 Jun;100(6):765-771. doi: 10.1007/s00128-018-2341-5. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29700581
-
Plant Extracts and Isolated Compounds Reduce Parameters of Oxidative Stress Induced by Heavy Metals: An up-to-Date Review on Animal Studies.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(16):1799-1815. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200407163408. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 32264808 Review.
-
Effects of heavy metals on fish physiology - A review.Chemosphere. 2022 Aug;300:134519. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134519. Epub 2022 Apr 6. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 35398071 Review.
Cited by
-
Coloured ornamental traits could be effective and non-invasive indicators of pollution exposure for wildlife.Conserv Physiol. 2016 Aug 26;4(1):cow028. doi: 10.1093/conphys/cow028. eCollection 2016. Conserv Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27766151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of pollution of Ganga River water using fish as bioindicator.Environ Monit Assess. 2016 Aug;188(8):444. doi: 10.1007/s10661-016-5433-x. Epub 2016 Jul 2. Environ Monit Assess. 2016. PMID: 27370309
-
Mitigation potential of selenium nanoparticles and riboflavin against arsenic and elevated temperature stress in Pangasianodon hypophthalmus.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 21;10(1):17883. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74911-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33087779 Free PMC article.
-
Content of Pb and Zn in Sediments and Hydrobionts as Ecological Markers for Pollution Assessment of Freshwater Objects in Bulgaria-A Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Aug 4;19(15):9600. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19159600. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35954957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective effects of dietary borax in the brain tissue of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) exposed to copper-induced toxicity.Fish Physiol Biochem. 2018 Oct;44(5):1409-1420. doi: 10.1007/s10695-018-0530-0. Epub 2018 Jun 29. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29959587 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Wang WX. Interaction of trace metals and different marine food chains. Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 2002;243:295–309.
-
- Dautremepuits C, Paris-Palacios S, Betoulle S, Vernet G. Modulation in hepatic and head kidney parameters of carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) induced by copper and chitosan. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2004;137:325–33. - PubMed
-
- Kalay M, Ay P, Canil M. Heavy metal concentration in fish tissues from the northeast Meditereansea. Bull Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1999;63:673–671. - PubMed
-
- Ashraf W. Accumulation of heavy metals in kidney and heart tissues of Epinephelus microdon fish from the Arabian Gulf. Environ Monit Assess. 2005;101:311. - PubMed
-
- Alinnor IJ. Assessment of elemental contaminants in water and fish samples from Aba River. Environ Monit Assess. 2005;102:15–25. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
