The impact of plasma high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels on cardiovascular risk stratification of hypertensive patients: results of the ICEBERG study
- PMID: 17617758
- PMCID: PMC8109927
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2007.05738.x
The impact of plasma high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels on cardiovascular risk stratification of hypertensive patients: results of the ICEBERG study
Abstract
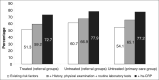
The Intensive/Initial Cardiovascular Examination Regarding Blood Pressure Levels: Evaluation of Risk Groups (ICEBERG) study focused on the impact of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) measurement on cardiovascular risk evaluation. The ICEBERG study comprised 2 subprotocols. Each subprotocol had 2 patient profiles: patients previously diagnosed with essential hypertension and under medical treatment and patients with systolic blood pressure 130 mm Hg or higher, or diastolic blood pressure 85 mm Hg or higher, with no treatment for at least 3 months before inclusion. Measurement of hs-CRP and cardiovascular risk stratification were performed according to European Society of Hypertension/European Society of Cardiology (ESH/ESC) guidelines. A total of 1817 patients were analyzed. In 1 group, the percentage of patients in "high" plus "very high" added-risk groups increased from 59.2% to 72.7% when hs-CRP data were added to routine serum biochemistries. In another, the increase was from 66.9% to 77.9%, whereas in a third group, it changed from 65.1% to 77.2%. The use of plasma hs-CRP levels might help in stratifying hypertensive patients into specific risk groups and modifying preventive approaches.
Figures

Comment in
-
Commentary on ICEBERG.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2007 Jul;9(7):557. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2007.07327.x. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2007. PMID: 17617767 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Intensive cardiovascular examination regarding blood pressure levels: evaluation of risk groups. ICEBERG study.Blood Press. 2006;15(5):291-301. doi: 10.1080/08037050600996644. Blood Press. 2006. PMID: 17380847
-
Impact of dyslipidemia on cardiovascular risk stratification of hypertensive patients and association of lipid profile with other cardiovascular risk factors: results from the ICEBERG study.Integr Blood Press Control. 2008;1:5-13. doi: 10.2147/ibpc.s3809. Epub 2008 Nov 2. Integr Blood Press Control. 2008. PMID: 21949610 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular risk stratification according to the 2003 ESH-ESC guidelines in uncomplicated patients with essential hypertension: comparison with the 1999 WHO/ISH guidelines criteria.Blood Press. 2004;13(3):144-51. doi: 10.1080/08037050410033169. Blood Press. 2004. PMID: 15223722
-
C-reactive protein and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein: an update for clinicians.Postgrad Med. 2011 Jan;123(1):114-9. doi: 10.3810/pgm.2011.01.2252. Postgrad Med. 2011. PMID: 21293091 Review.
-
Efficacy of Zofenopril vs. Irbesartan in Combination with a Thiazide Diuretic in Hypertensive Patients with Multiple Risk Factors not Controlled by a Previous Monotherapy: A Review of the Double-Blind, Randomized "Z" Studies.Adv Ther. 2017 Apr;34(4):784-798. doi: 10.1007/s12325-017-0497-8. Epub 2017 Mar 4. Adv Ther. 2017. PMID: 28260186 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Accuracy of retinal changes in predicting microalbuminuria among elderly hypertensive patients: a cross-sectional study from a teaching hospital in South India.Int Urol Nephrol. 2009;41(1):137-43. doi: 10.1007/s11255-008-9452-6. Epub 2008 Sep 3. Int Urol Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 18766459
-
Commentary on ICEBERG.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2007 Jul;9(7):557. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2007.07327.x. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2007. PMID: 17617767 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Genetic polymorphisms and plasma concentrations of leptin (rs7799039) and adiponectin (rs17300539) are associated with obesity in children and adolescents.Rev Paul Pediatr. 2022 Jun 10;40:e2021030. doi: 10.1590/1984-0462/2022/40/2021030IN. eCollection 2022. Rev Paul Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35703718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manabe S, Okura T, Watanabe S, et al. Association between carotid haemodynamics and inflammation in patients with essential hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 2005;19:787–791. - PubMed
-
- Schindler TH, Nitzsche EU, Olschewski M, et al. Chronic inflammation and impaired coronary vasoreactivity in patients with coronary risk factors. Circulation. 2004;110:1069–1075. - PubMed
-
- Mazer SP, Rabbani LE. Evidence for C‐reactive protein's role in (CRP) vascular disease: atherothrombosis, immuno‐regulation and CRP. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2004;17:95–105. - PubMed
-
- Rattazzi M, Puato M, Faggin E, et al. C‐reactive protein and interleukin‐6 in vascular disease: culprits or passive bystanders? J Hypertens. 2003;21:1787–1803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

