Mesangial cells of lupus-prone mice are sensitive to chemokine production
- PMID: 17617918
- PMCID: PMC2206365
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2226
Mesangial cells of lupus-prone mice are sensitive to chemokine production
Abstract
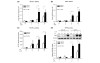
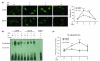
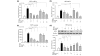
Infectious antigens may be triggers for the exacerbation of systemic lupus erythematosus. The underlying mechanism causing acceleration and exacerbation of lupus nephritis (LN) is largely unknown. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is capable of inducing an accelerated model of LN in NZB/W mice, featuring diffuse proliferation of glomerular resident cells. We hypothesized that mesangial cells (MCs) from LN subjects are more responsive to LPS than normal subjects. Cultured primary NZB/W and DBA/W (nonautoimmune disease-prone strain with MHC class II molecules identical to those of NZB/W) MCs were used. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and osteopontin (OPN) expressions either in the baseline (normal culture) condition or in the presence of LPS were evaluated by real-time PCR, ELISA, or western blot analysis. NF-kappaB was detected by ELISA, electrophoresis mobility-shift assay, and immunofluorescence. First, either in the baseline condition or in the presence of LPS, NZB/W MCs produced significantly higher levels of MCP-1 and OPN than the DBA/W MC controls. Second, NZB/W MCs expressed significantly higher levels of Toll-like receptor 4, myeloid differentiation factor 88, and NF-kappaB than the DBA/W MC controls, both receiving exactly the same LPS treatment. In conclusion, NZB/W MCs are significantly more sensitive than their normal control DBA/W MCs in producing both MCP-1 and OPN. With LPS treatment, the significantly elevated levels of both chemokines produced by NZB/W MCs are more likely due to a significantly greater activation of the Toll-like receptor 4-myeloid differentiation factor 88-associated NF-kappaB pathway. The observed abnormal molecular events provide an intrarenal pathogenic pathway involved in an accelerated type of LN, which is potentially infection triggered.
Figures
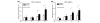
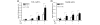
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

