The development of hypocretin (orexin) deficiency in hypocretin/ataxin-3 transgenic rats
- PMID: 17618058
- PMCID: PMC2042962
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.05.029
The development of hypocretin (orexin) deficiency in hypocretin/ataxin-3 transgenic rats
Abstract
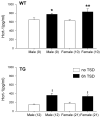
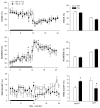
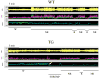
Narcolepsy is linked to a widespread loss of neurons containing the neuropeptide hypocretin (HCRT), also named orexin. A transgenic (TG) rat model has been developed to mimic the neuronal loss found in narcoleptic humans. In these rats, HCRT neurons gradually die as a result of the expression of a poly-glutamine repeat under the control of the HCRT promoter. To better characterize the changes in HCRT-1 levels in response to the gradual HCRT neuronal loss cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) HCRT-1 levels were measured in various age groups (2-82 weeks) of wild-type (WT) and TG Sprague-Dawley rats. TG rats showed a sharp decline in CSF HCRT-1 level at week 4 with levels remaining consistently low (26%+/-9%, mean+/-S.D.) thereafter compared with WT rats. In TG rats, HCRT-1 levels were dramatically lower in target regions such as the cortex and brainstem (100-fold), indicating decreased HCRT-1 levels at terminals. In TG rats, CSF HCRT-1 levels significantly increased in response to 6 h of prolonged waking, indicating that the remaining HCRT neurons can be stimulated to release more neuropeptide. Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep in TG rats (n=5) was consistent with a HCRT deficiency. In TG rats HCRT immunoreactive (HCRT-ir) neurons were present in the lateral hypothalamus (LH), even in old rats (24 months) but some HCRT-ir somata were in various stages of disintegration. The low output of these neurons is consistent with a widespread dysfunction of these neurons, and establishes this model as a tool to investigate the consequences of partial hypocretin deficiency.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expression of a poly-glutamine-ataxin-3 transgene in orexin neurons induces narcolepsy-cataplexy in the rat.J Neurosci. 2004 May 5;24(18):4469-77. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5560-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15128861 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between CSF hypocretin levels and hypocretin neuronal loss.Exp Neurol. 2003 Dec;184(2):1010-6. doi: 10.1016/S0014-4886(03)00388-1. Exp Neurol. 2003. PMID: 14769395
-
Hypocretin-2-saporin lesions of the lateral hypothalamus produce narcoleptic-like sleep behavior in the rat.J Neurosci. 2001 Sep 15;21(18):7273-83. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-18-07273.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11549737 Free PMC article.
-
Hypocretin (orexin): role in normal behavior and neuropathology.Annu Rev Psychol. 2004;55:125-48. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.55.090902.141545. Annu Rev Psychol. 2004. PMID: 14744212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sleep, sleep disorders and hypocretin (orexin).Sleep Med. 2004 Jun;5 Suppl 1:S2-8. doi: 10.1016/s1389-9457(04)90001-9. Sleep Med. 2004. PMID: 15301991 Review.
Cited by
-
Optogenetic examination identifies a context-specific role for orexins/hypocretins in anxiety-related behavior.Physiol Behav. 2014 May 10;130:182-90. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2013.10.005. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Physiol Behav. 2014. PMID: 24140988 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of saporin-induced lesions of three arousal populations on daily levels of sleep and wake.J Neurosci. 2007 Dec 19;27(51):14041-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3217-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 18094243 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of sleep on the cardiovascular and thermoregulatory systems: a possible role for hypocretins.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010 Oct;109(4):1053-63. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00516.2010. Epub 2010 Aug 12. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010. PMID: 20705949 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models of sleep disorders.Comp Med. 2013 Apr;63(2):91-104. Comp Med. 2013. PMID: 23582416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orexin receptor subtype activation and locomotor behaviour in the rat.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2010 Mar;198(3):313-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2009.02056.x. Epub 2009 Nov 4. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2010. PMID: 19889100 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arias-Carrion O, Drucker-Colin R, Murillo-Rodriguez E. Survival rates through time of hypocretin grafted neurons within their projection site. Neurosci Lett. 2006;404:93–97. - PubMed
-
- Chemelli RM, Willie JT, Sinton CM, Elmquist JK, Scammell T, Lee C, Richardson JA, Williams SC, Xiong Y, Kisanuki Y, Fitch TE, Nakazato M, Hammer RE, Saper CB, Yanagisawa M. Narcolepsy in orexin knockout mice: molecular genetics of sleep regulation. Cell. 1999;98:437–451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

